Categories
- Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)(2)
- 1
Description of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Surge Protection Devices (SPDs) are designed to safeguard electrical systems by limiting transient voltages, either by diverting or suppressing surge currents, and is capable of performing these functions repeatedly as defined by its specifications. Historically, SPDs have been referred to as Transient Voltage Surge Suppressors (TVSS) or Secondary Surge Arrestors (SSA).
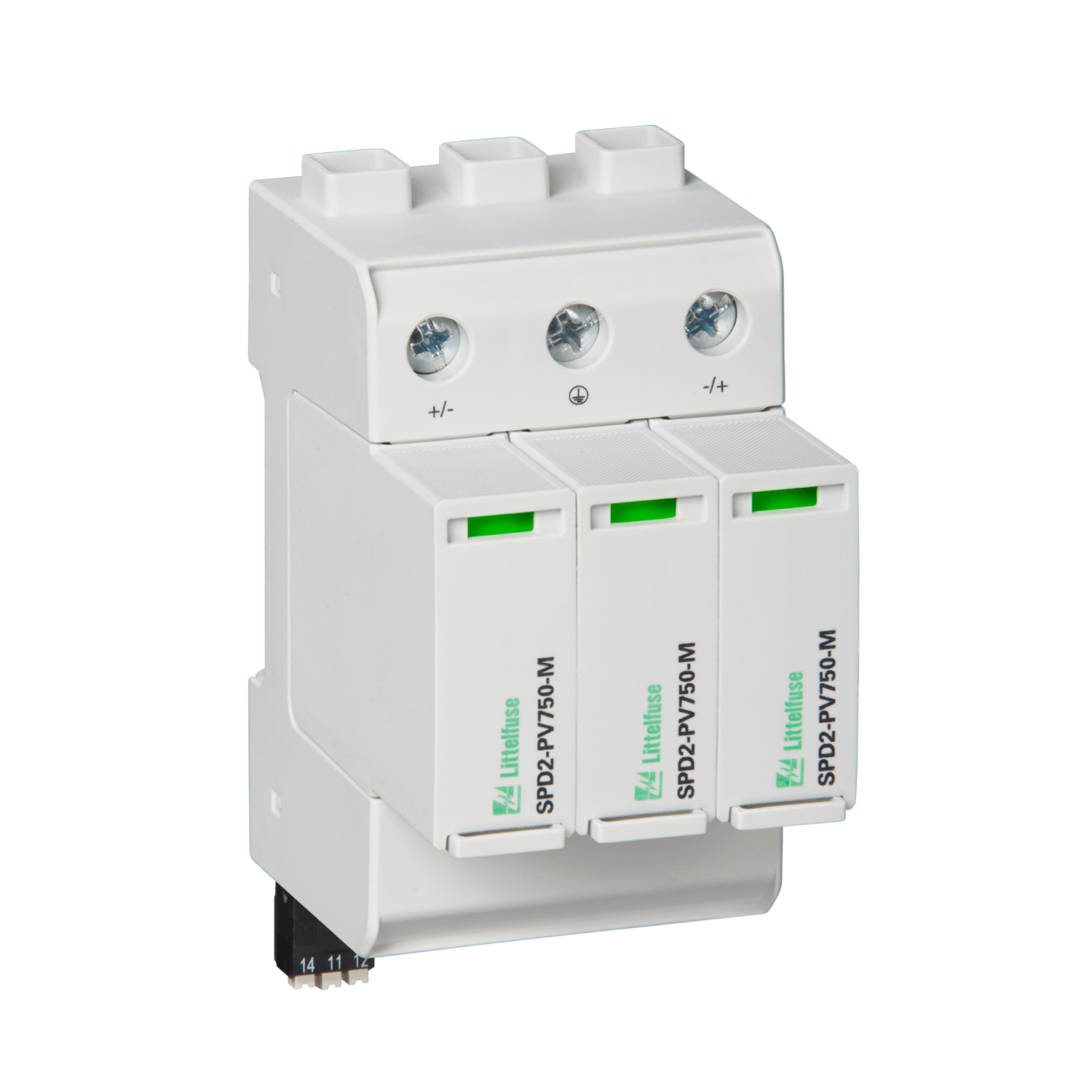

Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
Working Principle of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
At its core, a Surge Protective Device (SPD) functions by limiting transient voltages on the protected circuit and redirecting the surge current back to its source or to the ground. For an SPD to operate effectively, it must include at least one non-linear component that can switch between high and low impedance states under varying conditions.
Under normal operating voltages, the SPD remains in a high-impedance state, which means it does not interfere with the system. However, when a transient voltage occurs, the SPD transitions into a conduction state (low impedance), allowing it to divert the surge current away from the circuit. This action effectively clamps the voltage to a safer level. Once the transient event has passed, the SPD automatically resets to its high-impedance state, ready to protect against future surges.
Applications of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
- Industrial Settings: Power distribution systems, control panels, programmable logic controllers, electronic motor controllers.
- Commercial Environments: Medical equipment, critical load protection, backup power systems, uninterruptible power supplies and communication circuits.
- Residential Spaces: Home automation and entertainment systems, telephone and fax lines, cable TV feeds, security and alarm systems.
Types of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
1. Type 1 SPDs are positioned at the primary entry point, such as the main distribution board.
2. Type 2 SPDs are placed at secondary distribution points, like sub-distribution boards.
Combined Type 1 & 2 SPDs are available for installation in consumer units, offering protection at both the origin and sub-distribution levels.
3. Type 3 SPDs are designed to be installed in close proximity to the equipment they are protecting and should be used as a supplementary measure to Type 2 SPDs.
Benefits of Surge Protection Devices (SPDs)
- Protection of electrical installations from damage caused by transient overvoltages.
- Prevention of instant failure or long-term damage to sensitive electronic equipment.
- Compliance with safety standards and regulations.
- Potential cost savings by preventing expensive damage to electrical systems and equipment.