Categories
- (ASIC)Application-Specific Integrated Circuit(2,645)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 133
What Is ASIC?
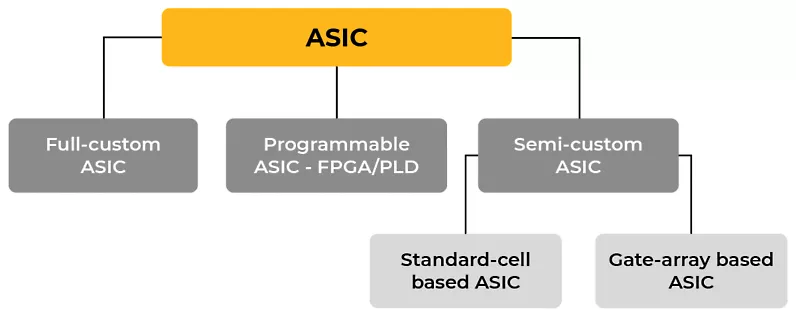
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) is an integrated circuit that's designed for a specific task or use case. Unlike field-programmable gate array (FPGA) boards, ASICs are designed from the start to meet specific requirements exactly. There are two main ways to design an ASIC: gate array and full customization.
Gate-array designs use a semi-custom approach, using pre-determined layers, transistors, and other active components to make the upfront design process and associated costs simpler.
On the other hand, full-custom designs are more complex and expensive, but they offer unmatched chip versatility and the ability to efficiently handle heavier workloads.
Types of ASIC Design
Advantages of ASIC :
Best performance. ASICs are made to do one thing really well, with only the parts needed for that one thing. This design is more efficient and performs better than general-purpose processors.
Energy efficiency: ASICs can remove unnecessary components, making them more power-efficient and reducing energy waste.
Space-saving design: ASICs can be made to fit specific shapes, making electronic devices more space-efficient.
Cost-effective for mass production. ASICs are expensive to make at first, but they get cheaper as more are made. ASICs are cost-effective because they don't have any unnecessary parts. This makes them good for high-volume applications.
Improving performance and efficiency: The electronics industry is always looking for ways to improve performance and efficiency. ASICs are used in many different applications, which helps to develop new technology. To make the design process faster and cheaper, it is important to choose the right software. As technology gets faster and smaller, designers must find new ways to make it work.