

AC Power Supply and Appliance
Catalog
4 Sources of AC Power Supply at HomeThe Basic Power Distribution GridAutomatic Power Supply Source Selection at HomesAutomatic Power Supply Selection with MicrocontrollerFrequently Ask QuestionsEver wondered how electricity gets to your home? Or how you still have power when there's an outage? There are actually several ways to keep your AC power supply running without having to go without electricity.
4 Sources of AC Power Supply at Home
AC Mains: AC power is commonly used for home electricity because it’s easy to transmit, inexpensive, and simple to convert to DC. But have you ever stopped to think about how this whole power distribution system works? No worries—let me break it down for you.
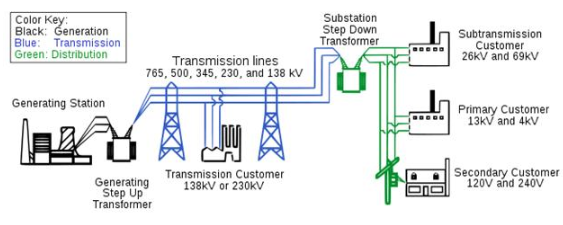
Power Distribution System
The Basic Power Distribution Grid
The power distribution grid is made up of several key components:
Power Plant: The power plant is where 3-phase AC power is generated. The reason for using three phases is that the currents in each phase cancel each other out, which helps maintain a balanced load. This setup also creates a rotating magnetic field, which is essential for electric motors. Power plants usually rely on steam turbine generators, which get their steam from burning coal, oil, natural gas, or from nuclear power. The AC power generated is then stepped up to a high voltage (around 155 kV) using large transformers.
Transmission Substations: The high-voltage power (155 kV) from the power plant is sent to transmission substations. These substations are equipped with step-down transformers, circuit breakers, and control systems that reduce the voltage to 60 kV, making it suitable for feeding into transmission lines.
Transmission Unit: The transmission unit consists of towers carrying 3-phase power, with a fourth wire used as a ground to protect against lightning strikes. Typically, the power is transmitted over a distance of around 400 km.
Distribution Grid: The distribution grid includes step-down transformers that lower the 60 kV power to 12 kV, along with buses that help distribute the AC power across the network.
Transmission Units to Home: The transmission units consist of 3-phase towers that carry the AC power. These towers also have regulator banks to smooth out voltage fluctuations, and taps that allow single-phase or 2-phase power to be drawn from the 3-phase supply.
AC Power Unit Near Homes: Close to homes, the AC power is further stepped down by transformers on electric poles, reducing the voltage to 240V for home use. This 240V supply consists of three wires: two carry 120V each with a 180-degree phase difference, and the third is a neutral or ground wire.
Solar Power: An additional option for home power is solar energy, which is becoming a popular and sustainable source of energy. Solar power systems at homes typically include the following components:
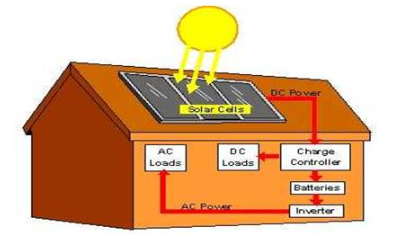
Solar Power to Homes
Solar Panels: Solar panels, made up of solar cells, are installed on the roof of homes. They're positioned to capture the maximum amount of sunlight and convert it into electrical energy.
Charge Controller: The charge controller manages the charging process for the batteries, preventing excess DC voltage from flowing into them. It also ensures that the batteries are charged properly, especially when the power supply runs low.
Batteries: Typically, a set of around 12 batteries is used to store the DC energy generated by the solar panels.
Inverter: The inverter is responsible for converting the DC power stored in the batteries into the AC power needed to run home appliances that require AC for operation.
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS): Just like with solar power, the same system can be applied to AC power from the mains. A UPS can store power and convert AC to DC for storage, then back to AC when needed, providing a continuous power supply during outages.
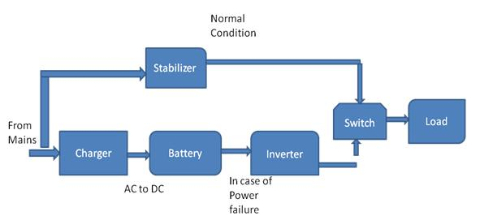
Uninterrupted Power Supply System
Normal Mode: In normal operation, power is supplied from the AC mains and regulated by a stabilizer before being provided to the connected devices. This AC voltage is then converted into DC voltage to charge the batteries.
Backup Mode: When backup power is needed, the stored DC power in the batteries is converted back into AC power using an inverter. A basic inverter consists of a transformer with a center-tapped primary winding, along with switches that allow current to flow back to the battery through the primary windings. This process generates an AC voltage across the primary windings, supplying power to the loads.

A Practical UPS
Generators: A home backup generator typically runs on natural gas or diesel. It includes a controller that monitors the current flow from the mains supply through an automatic transfer switch. If a power outage occurs, the automatic transfer switch disconnects the mains and connects the generator. After about 10 seconds of the outage, the generator starts up and supplies power to the home appliances. When the main power returns, the controller detects it and automatically shuts off the generator, switching back to the main supply.
While generators are generally more affordable and consume less power, they tend to be noisier compared to inverters.
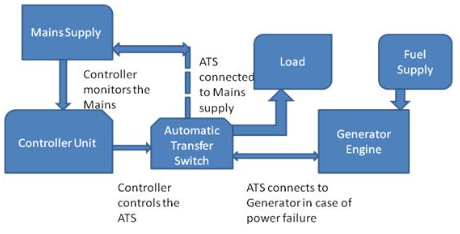
AC Backup Generator System

A Practical Generator used at Homes
Automatic Power Supply Source Selection at Homes
You can create a simple automatic system to select the available power supply source at home. The system requires a basic microcontroller, a relay driver, and 4 relays.
The setup includes 4 push buttons connected to the microcontroller, each representing the status of a different power source. Based on the button input, the microcontroller controls the relay driver to activate the correct relay, thereby selecting the appropriate power source for use.
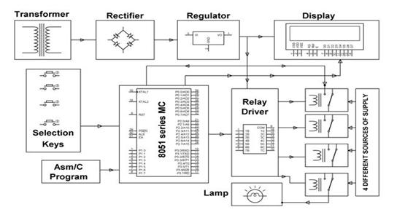
Block Diagram showing Automatic Selection of AC Power Supply
Automatic Power Supply Selection with Microcontroller
In normal operation, the microcontroller controls the relay driver to connect the load to the Mains supply through the corresponding relay. When the first push-button (representing the Mains supply) is pressed, it indicates a failure in the Mains supply. In response, the microcontroller is programmed to send a high logic signal to one of the input pins of the relay driver, which is connected to the corresponding alternate power source. The relay driver then outputs a low logic signal at its corresponding pin, activating the relay connected to the alternate power source and providing power to the load.
If both the Mains supply and the adjacent alternate power source fail, the system automatically switches to the next available power supply. For example, if the Mains supply button and its adjacent alternate source button are pressed, the system will switch to the power source corresponding to the third push button.
An LCD can be used to display the current load condition, making it easy to monitor which power supply is being used.
Frequently Ask Questions
What power supply do I need for an air conditioner?
The power requirements for an air conditioner depend on the type of unit. Window units typically run on 110/120 volts, while central or mini-split systems need 208/240 volts. Wattage varies significantly by size, with window units using between 500 and 1,500 watts, and central units requiring 3,000 to 5,000 watts. Don't forget to factor in the higher "startup" wattage, which can be two to three times the normal running wattage—this is especially important when choosing a generator.
What household appliances use AC power?
As mentioned earlier, most household electronics run on AC power, and this applies to businesses and offices too. Common household appliances that use AC power include refrigerators, air conditioners, washing machines, and other large appliances, as well as systems that require high power and long-distance transmission.
What are the three types of AC power sources?
The three main types of AC power sources are single-phase AC, three-phase AC, and portable AC power sources. Single-phase AC is commonly used in homes and small businesses, while three-phase AC is more common for larger operations and industrial use.
What household items use an AC power cord?
AC power is the standard form of electricity delivered through power grids, and it’s used to power many household items, including large appliances, lighting systems, motors, and other electronics. Examples include refrigerators, freezers, and industrial appliances.
What is the most common source of AC power?
Most AC power comes from rotating field generators, although rotating armature generators can also be used. These generators are linked to electrical distribution systems that supply power to homes and businesses.
Does AC need its own breaker?
Yes, circuit breakers are designed to protect your home's electrical system by shutting off the power when there’s an overload. Your air conditioner should have its own dedicated circuit to prevent overloading and reduce the risk of safety hazards.
What are five devices that use AC power?
AC power is the most common type of electricity used to run electric motors, which convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. Common household devices that rely on AC power include refrigerators, dishwashers, garbage disposals, toaster ovens, and air conditioning units.
How do I know which AC adapter to buy?
To choose the right AC adapter for your device, make sure the electrical ratings match. The device’s input voltage and current should align with the adapter's output voltage and current. Check the product label or user manual of your device for the correct voltage and current specifications.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













