

How Do Distance Sensors Work and Where Are They Used?
Catalog
What Is a Distance Sensor?How Do Distance Sensors Work?How to Choose the Right Distance Sensor?LED-Based Sensors – Pros & ConsApplications of Distance SensorsFrequently Ask QuestionsThere are various methods available to measure the distance to an object, each based on different types of hardware. Distance sensors utilize a wide range of technologies such as laser, infrared (IR) triangulation, ultrasonic waves, and LED time-of-flight (TOF). The choice of sensor depends largely on the specific application. Each type offers unique performance characteristics, including operating range, resolution, frequency, field of view (FOV), response time, installation complexity, and cost.
This article provides an introduction to how distance sensors function and explores their common applications.

What Is a Distance Sensor?
A distance sensor is a dependable device used in a wide range of applications that require precise and rapid measurements, accurate positioning, and detection of various materials. Common uses include monitoring coil unwinding, detecting double sheets, and ensuring the precise positioning of high-bay stackers.
How Do Distance Sensors Work?
Distance sensors typically operate by emitting a type of wave—such as laser, infrared (IR) light, or ultrasonic sound—and then measuring how the wave changes when it reflects back from an object. These changes can be analyzed based on the signal’s return time, intensity, or phase shift. Key performance factors for distance sensors include resolution, detection range, and update rate.
When integrating a distance sensor into a project, several factors should be considered, such as the sensor type, required response speed, power consumption, and the length of the cable between the sensor and the control board.
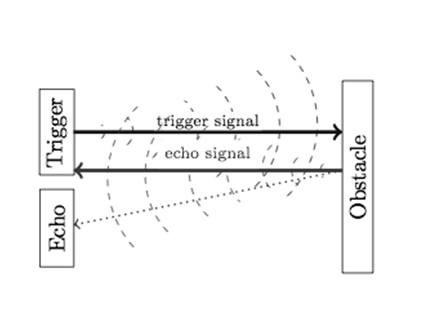
distance-sensor-working
How to Choose the Right Distance Sensor?
There are many distance sensing technologies to choose from, depending on your project needs. The most commonly used types include basic LED-based sensors, LIDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and VCSEL-based sensors. Each has its strengths and limitations.
To help you choose the right one, we provide tutorials, project examples, and comparison tools. These sensors are known for being reliable, cost-effective, easy to set up, and capable of accurate, non-contact distance measurements—making them ideal for a variety of automation applications.
LED-Based Sensors – Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Low cost
- Compact size x
- Decent update rate
- Multiple interface options
Cons:
- High power consumption
- Limited maximum range
LIDAR Sensors – Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Excellent long-range detection
- Extremely fast update rate
Cons:
- Expensive
- Larger physical size
- High power consumption
Ultrasonic Sensors – Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Very low power consumption
- Offers various interface options
Cons:
- Low resolution
- Slow refresh rate
VCSEL Sensors – Pros & Cons
Pros:
- Wide input voltage range
- Good resolution
- Affordable cost
Cons:
- Limited to I2C interface
- Very short maximum detection range
Applications of Distance Sensors
Distance sensors are used in a wide variety of applications that require accurate positioning and fast, non-contact measurement. Some common uses include:
- Measuring distance and positioning on robotic grippers for pick-and-place tasks
- Palletizing and item placement operations
- Measuring coil diameters in production lines
- Detecting components and small parts in automated systems
- Monitoring stack heights, identifying double sheets, and measuring wood thickness in packaging and material handling industries
In summary, distance (or proximity) sensors are essential tools for fast and precise measurement, positioning, and object detection across a wide range of materials. They offer reliable performance in many industrial and automation applications—such as tracking coil unwinding and detecting overlapping sheets.
Frequently Ask Questions
How do distance sensors work?
Ultrasonic distance sensors detect how far an object is by emitting high-frequency sound pulses and calculating the time it takes for the echo to return. By using the known speed of sound, the sensor determines the object's distance.
What type of sensor is ideal for measuring distance?
Infrared (IR) Sensors: These sensors estimate distance by sending out infrared light and analyzing the reflected signal. They’re commonly found in applications such as remote controls and short-range object detection.
What are the two common types of distance sensors?
Distance sensors generally fall into two main categories:
- Ultrasonic Sensors, which rely on sound waves
- Infrared Sensors, which use infrared light Both are widely used for object detection and distance measurement in industrial and consumer electronics.
Which sensor is suitable for long-range distance detection?
Sensors like radar, LIDAR, and ultrasonic models are typically used for measuring longer distances. These technologies provide reliable readings even over several hundred meters.
How precise are distance sensors?
At distances under 200mm, the measurement accuracy is around ±15mm. Beyond 200mm, accuracy improves to about 5%. Some sensors can also estimate object size—classifying it as small, medium, or large—which helps distinguish between walls and movable items. Additionally, certain sensors can track how fast an object is approaching.
Proximity Sensors vs. Distance Sensors: What’s the Difference?
How are proximity and distance sensors different?
While both sensors are used to detect objects, their purposes are slightly different:
- Distance sensors measure the exact distance between the sensor and an object.
- Proximity sensors simply detect whether an object is within a certain range, without indicating the specific distance.
Which sensor measures distance?
Ultrasonic distance sensors are commonly used for this purpose. These sensors emit high-frequency sound waves and measure how long it takes for the echo to bounce back. By calculating the time delay and knowing the speed of sound, they can accurately determine the distance to the object.
What sensors are used for proximity detection?
The most widely used proximity sensors include:
- Inductive proximity sensors – ideal for detecting metal objects
- Capacitive proximity sensors – suitable for detecting both metallic and non-metallic materials These sensors are commonly found in smartphones, factory automation systems, self-driving vehicles, and even in waste sorting systems.
LiDAR vs. Ultrasonic: Which is better for distance sensing?
LiDAR and ultrasonic sensors work on similar principles—both measure the time it takes for a signal to return—but they use different types of waves:
- LiDAR uses laser beams for high-precision measurements and object detection
- Ultrasonic uses sound waves and is generally more cost-effective but less precise over long distances LiDAR tends to offer better resolution and accuracy, especially for mapping and navigation.
What is the typical range of an ultrasonic sensor?
Ultrasonic sensors can detect objects and measure distances without contact, using the time-of-flight of sound waves. Depending on the model and environment, their detection range typically spans from a few centimeters up to several meters in open air.
Common Questions About Distance and Proximity Sensors
What is the maximum detection range of a proximity sensor?
Proximity sensors typically detect objects at short ranges, often within just a few millimeters. However, some advanced models—such as photoelectric proximity sensors—can detect small targets from distances of up to 60 meters, depending on sensor type and environmental conditions. These sensors vary in how they transmit and receive light, affecting their range and accuracy.
What is a radar distance sensor?
A radar distance sensor uses radio waves to detect and measure the distance to objects in its field of view. Radar sensors work in both horizontal and vertical directions and are well-suited for outdoor and industrial environments. Different radar frequencies offer different detection characteristics, making them adaptable for various applications—from traffic monitoring to level measurement in tanks.
What is a modular distance sensor?
A modular distance sensor is designed for use in vehicles and is typically installed between a vehicle’s speed sensor and a system like the RAC (Road Access Controller). It provides high-accuracy measurements—often within 1 foot per mile—and is generally easier to install than magnetic sensor systems. However, compatibility may vary depending on the vehicle model.
What is a following distance detector?
A following distance detector is a safety system used in vehicles to help drivers maintain a safe gap from the vehicle ahead. Using dash cams, AI-based distance estimation, and real-time speed data, it alerts drivers when their following distance is too short, encouraging safer driving behavior.
What is an ultrasonic distance sensor?
An ultrasonic distance sensor works by emitting high-frequency sound waves and measuring the time it takes for the echo to return after hitting an object. The time delay is used to calculate the distance between the sensor and the target. These sensors are commonly used in applications like robotics, obstacle detection, and liquid level measurement, especially when non-contact measurement is required.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













