
How Fingerprint Sensors Work and Where They're Used
Catalog
What Is a Fingerprint Sensor?R305 Fingerprint Sensor ModuleKey Features of a Fingerprint SensorWorking Principle of a Fingerprint SensorSpecifications of the Fingerprint SensorUsing a Fingerprint Sensor with ArduinoWiring the Fingerprint SensorWiring the Fingerprint Sensor and TFT Display to ArduinoProject Code OverviewHow It WorksFrequently Ask QuestionsOver the past few years, fingerprint recognition has become a common method for identification. Compared to other biometric technologies, fingerprint systems are generally faster, more cost-effective, and offer reliable performance. Each person's fingerprint is unique, formed by a pattern of ridges that create distinct whorls and loops.
Fingerprints are typically categorized into five main types: whorl, right loop, left loop, tented arch, and plain arch. One of the common challenges in fingerprint recognition systems is distinguishing between prints that belong to similar pattern types.
To address this, various recognition systems—often powered by neural networks—are used to analyze ridge endings and minutiae points to accurately match a fingerprint to its identity.
What Is a Fingerprint Sensor?
A fingerprint sensor is a type of sensor used in fingerprint recognition devices. These sensors are typically built into fingerprint modules and are widely used for computer and data security.
The key advantages of fingerprint sensors include high accuracy, reliable performance, and durability—thanks to advanced biometric fingerprint technology. Fingerprint scanners or readers offer a safer and more convenient alternative to traditional passwords, which can be easily guessed or forgotten.
That’s why it’s better to use a USB-based fingerprint reader or scanner with biometric software for verification, identification, and authentication. Your fingerprint acts like a digital password—but one that can’t be forgotten, lost, or stolen.
R305 Fingerprint Sensor Module
There are several types of fingerprint modules available on the market, such as the R305 and R307. To better understand how these sensors work, let’s take a closer look at the R305 fingerprint sensor module.
The R305 is a fingerprint sensor module commonly used in biometric security systems for fingerprint detection and verification. It’s often found in devices like safes, where it plays a key role in secure access control.
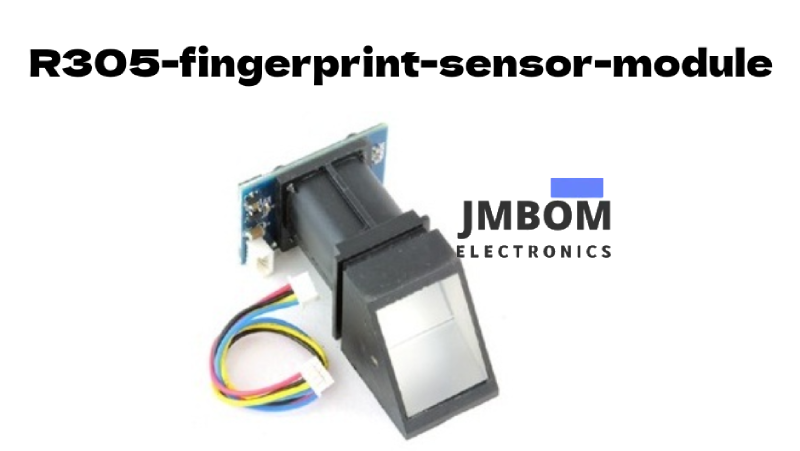
This module includes a high-performance DSP chip that handles image processing, feature extraction, matching, and calculation. It can be connected to any microcontroller via a TTL serial interface, which allows it to send and receive data packets—such as fingerprint images, scan commands, search requests, and hash results.
New fingerprints can be enrolled and stored directly in the module’s onboard flash memory.
Key Features of a Fingerprint Sensor
- Combines fingerprint image capture with an integrated chip-level algorithm
- Compact design allows for easy integration into a wide range of end products
- Low power consumption, high performance, small size, and cost-effective
- Uses advanced optical technology and precise module development techniques
- Strong image processing capabilities, able to capture fingerprint images at up to 500 dpi resolution
Working Principle of a Fingerprint Sensor
The operation of a fingerprint sensor is based on fingerprint processing, which involves two main steps: enrollment and matching.
During enrollment, the user places their finger on the sensor—usually twice—so the system can capture high-quality images. It then processes these images to create a unique fingerprint template, which is stored in memory.
During matching, the user places their finger on the optical sensor again. The system captures a new image, generates a pattern from it, and compares this pattern with the stored templates.
- In 1:1 matching, the system compares the scanned fingerprint with one specific stored template.
- In 1:N matching, the system scans all stored templates in the database to find a match.
In both cases, the sensor returns a result—either a successful match or a failure—based on the comparison.
Specifications of the Fingerprint Sensor
- Sensor Type: Optical
- Interface: USB 1.1 / TTL logic level (UART)
- Scanning Speed: 0.5 seconds
- Verification Speed: 0.3 seconds
- Storage Capacity: Up to 1,000 fingerprint templates
- Security Level: 5
- Baud Rate (RS232): Adjustable from 4800 to 115200 bps
- Operating Current: Typically 50 mA, peak 80 mA
- Matching Method: 1:N (one-to-many)
- Indicator: Bright green backlight, 15KV ESD protection
- Sensor Lifespan: Up to 100 million operations
- Dimensions: 44.1 × 20 × 23.5 mm
- Character File Size: 256 bytes
- Template Size: 512 bytes
- FRR (False Rejection Rate): < 1.0%
- FAR (False Acceptance Rate): 0.001%
- Operating Voltage: 4.2V to 6.0V DC
- Operating Temperature Range: -20°C to +40°C
Using a Fingerprint Sensor with Arduino
To demonstrate a simple application of the fingerprint sensor, here’s an example project: a fingerprint-based security system using an Arduino board.
Required Components
- Arduino Nano board
- R305 Fingerprint sensor module
- TFT display
- Small breadboard
- Jumper wires (different colors for clarity)
- Power bank (for portable power supply)
Wiring the Fingerprint Sensor
The fingerprint sensor module has five pins: DNC, VCC, TX, RX, and GND. These are connected to the Arduino using colored jumper wires for easy identification:
- DNC → White wire
- VCC → Red wire (connected to 5V on Arduino)
- TX → Blue wire (connects to Arduino RX)
- RX → Green wire (connects to Arduino TX)
- GND → Black wire (connects to Arduino GND)
This setup allows the Arduino to communicate with the fingerprint sensor and display messages or statuses on the TFT screen.
Wiring the Fingerprint Sensor and TFT Display to Arduino
Fingerprint Sensor Module to Arduino Connections:
- Black wire (GND) → Connect to Arduino GND
- Red wire (VCC) → Connect to Arduino 5V
- Green wire (RX) → Connect to Arduino Digital Pin 2
- White wire (TX) → Connect to Arduino Digital Pin 3
Note: Pin 2 and Pin 3 on Arduino are commonly used for software serial communication with the sensor.
TFT Display to Arduino Connections:
- VCC → Connect to Arduino 5V
- GND → Connect to Arduino GND
- CS → Connect to Digital Pin 10
- RST → Connect to Digital Pin 9
- A0 (also known as DC) → Connect to Digital Pin 8
- SDA (MOSI) → Connect to Digital Pin 11
- SCK → Connect to Digital Pin 13
- LED → Connect to Arduino 3.3V
Make sure the display module supports 5V logic levels, or use level shifters if needed for 3.3V compatibility.
Project Code Overview
To run this fingerprint sensor project with a display, you'll need to install the following libraries:
- Adafruit Fingerprint Sensor Library
- Adafruit GFX Library
- Sumotoy's TFT Display Library
Step 1: Enroll Fingerprints
Start by uploading the Enroll example to your Arduino board:
Go to File → Examples → Adafruit Fingerprint Sensor Library → Enroll
This example allows you to register fingerprints and save them to the sensor’s internal flash memory. Once uploaded, open the Serial Monitor. The program will prompt you to place your finger twice on the sensor to complete the enrollment process.
You can enroll multiple fingerprints this way.
Sample Code Snippet
Here’s a simplified version of the code logic used in the main loop:
cppCopyEditvoid loop() {
fingerprintID = getFingerprintID(); // Scan the fingerprint
delay(50);
if (fingerprintID == 1) { // Match found for ID 1
display.drawBitmap(30, 35, icon, 60, 60, GREEN);
delay(2000);
displayUnlockedScreen();
displayIoanna(); // Show name or image
delay(5000);
display.fillScreen(BLACK);
displayLockScreen();
}
if (fingerprintID == 2) { // Match found for ID 2
display.drawBitmap(30, 35, icon, 60, 60, GREEN);
delay(2000);
displayUnlockedScreen();
displayNick(); // Show different name or image
delay(5000);
display.fillScreen(BLACK);
displayLockScreen();
}
}
How It Works
- Every 50 ms, the fingerprint sensor scans for input.
- If a fingerprint is recognized and matches an enrolled ID, the system displays a "WELCOME" message with a custom screen.
- After a few seconds, the screen automatically returns to the locked state, ready for the next scan.
This covers everything about the fingerprint sensor module, which is widely used for fingerprint detection and is very user-friendly for various projects. With this module, you can easily perform tasks like registration, fingerprint capture, searching, and matching. These sensors come with built-in flash memory to securely store fingerprint data.
Common applications of fingerprint sensors include mobile phones, access control systems, display authentication, security systems, time and attendance tracking, door locks, and more.
Now, here’s a question for you: What is the price of a fingerprint sensor?
Frequently Ask Questions
How Do Fingerprint Sensors Work?
Fingerprint sensors capture a unique image of your fingerprint and compare it to stored digital templates to verify your identity. There are several types of fingerprint sensors—optical, capacitive, and ultrasonic—each using different technology to capture the fingerprint’s details accurately.
Is It Safe to Use Fingerprint Authentication on Banking Apps?
Yes, banking apps with biometric login options are often safer than traditional online portals. Using your face, fingerprint, or phone for authentication makes it much harder for hackers to gain access compared to just a username and password.
Is a Fingerprint More Secure Than a Passcode?
Biometric authentication like fingerprints is generally more secure than passwords because it’s much harder for cybercriminals to steal or replicate. Biometrics are also resistant to phishing attacks and offer a more convenient user experience.
How Does Your Phone Recognize Your Finger?
Phones use one of three main technologies to read fingerprints: optical, capacitive, or ultrasonic.
- Optical sensors use a small camera to capture a fingerprint image, often illuminated by LEDs or the phone’s display.
- Capacitive sensors measure electrical signals from the ridges and valleys of your fingerprint.
- Ultrasonic sensors use high-frequency sound waves to create a detailed 3D image of your fingerprint.
What Is Device Fingerprinting (Google Fingerprinting)?
Device fingerprinting gathers information about your device and browser to create a unique profile. While it’s not designed specifically for advertising, this data can be used to deliver targeted ads based on your online behavior.
Is Face ID Better Than Fingerprint Authentication?
Both Face ID and fingerprint recognition (Touch ID) offer secure and convenient ways to unlock devices and approve transactions. Face ID is often seen as more convenient because it’s contactless and easy to use, while fingerprint sensors can be faster and more reliable in certain situations, like when wearing masks or gloves.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













