
What is an Infrared Sensor (IR)?
Catalog
What Is an IR Sensor?Types Of IR Sensor What Are The Differences Between Passive Sensors, Active Sensors, And Image Sensors?How Does an IR Sensor Work?Advantages Of IR SensorsDisadvantages of IR SensorsApplications of IR Sensors
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Final Thoughts Frequently Ask Questions
Today, infrared technology is widely used in various wireless applications, primarily for object sensing and remote control purposes.In the electromagnetic spectrum, infrared is divided into three segments: the near-infrared region, the mid-infrared region, and the far-infrared region.In this blog, we will explore the working principle of IR sensors and their applications.

What Is an IR Sensor?
An IR sensor, or infrared sensor, is an designed to detect specific characteristics in its environment by emitting or detecting infrared radiation. These sensors can measure the heat of a target and its motion. In many electronic devices, the IR sensor circuit is a crucial module, functioning similarly to human vision by identifying obstacles.
A typical infrared detection system consists of five basic elements: an infrared source, a transmission medium, optical components, infrared detectors or receivers, and signal processing. Infrared lasers and infrared LEDs of specific wavelengths serve as the infrared sources.
The three primary types of media for infrared transmission are vacuum, atmosphere, and optical fibers. Optical components are employed to focus infrared radiation or to restrict the spectral response.
A sensor that measures infrared radiation without emitting it is known as a PIR, or passive infrared sensor. In the infrared spectrum, the radiation from various targets and certain types of thermal radiation are invisible to the naked eye but can be detected by IR sensors.
In this type of sensor, an IR LED serves as the emitter, while a photodiode acts as the detector. When infrared light hits the photodiode, the output voltage and resistance change in relation to the intensity of the received IR light.
Types Of IR Sensor
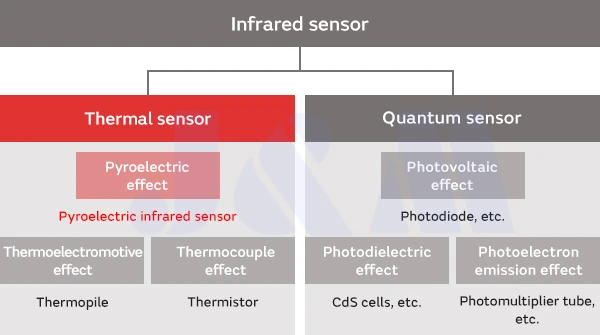
Infrared sensors can be broadly categorized into "thermal" and "quantum" types based on their operational principles. Thermal sensors convert infrared rays into heat, which then leads to changes in resistance and the term electromotive force that produces an output. In contrast, quantum sensors operate using the photoconductive effect related to the energy transitions of semiconductors and the photovoltaic effect in PN junctions. Pyroelectric infrared sensors are a specific type of thermal sensor.
What Are The Differences Between Passive Sensors, Active Sensors, And Image Sensors?
Human body detection is one application of pyroelectric infrared sensors. Generally, there are three types of human detection sensors, with pyroelectric infrared sensors categorized as passive sensors.

How Does an IR Sensor Work?
An IR Sensor operates similarly to an object detection sensor, with the main difference being that the IR sensor includes an LED and a photodiode for emitting and detecting signals. This combination creates what is known as an optocoupler or photo-coupler.
The infrared light-emitting diode (LED) is a specialized transmitter capable of emitting infrared radiation. While it resembles a standard diode, the radiation it produces is invisible to the human eye. The basic principle involves having infrared receivers on one side and transmitters on the other, where the receivers detect the radiation emitted by the IR transmitters.
The receivers are typically photodiodes, but these are not ordinary photodiodes. They only activate in the presence of infrared radiation. It’s also worth mentioning that IR receivers vary in terms of packaging, wavelength, voltage, and other factors.
For an infrared sensor to function effectively, both the transmitter (IR LED) and receiver (IR photodiode) must operate at the same wavelength. If the wavelengths differ, the photodiode will not respond to the infrared light emitted by the LED.
Advantages Of IR Sensors
The infrared sensor offers several advantages, including:
- Low power consumption
- Strong immunity to noise
- Ability to detect motion regardless of lighting conditions
- Resistance to rust
- Non-contact detection capability
- No data leakage due to the directional nature of infrared radiation
- Compact size and affordability
- Faster response time compared to thermocouples
- High reliability
Disadvantages of IR Sensors
However, infrared sensors also have some disadvantages:
- Requires a clear line of sight
- Performance can be affected by environmental conditions such as fog, rain, pollution, and dust
- Can be obstructed by common objects
- Slower data transmission rates
- Limited range
- High-intensity IR signals can be harmful to human eyes
Applications of IR Sensors
Infrared sensors are used in various applications, including:
- Rail safety
- IR imaging devices
- Infrared astronomy
- Optical power meters
- Night vision devices
- Sorting devices
- Moisture analyzers
- Missile guidance
- Flame monitors
- Remote sensing
- Climatology
- Gas analyzers
- Meteorology
- Photobiomodulation
- Petroleum exploration
- Anesthesiology testing
- Gas detection
- Water analysis
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1, What’s the Function of Infrared?
Infrared technology has a variety of applications beyond just heat sensing. It plays a significant role in networking, communication, thermal imaging, and even night vision devices. Whether wired or wireless, infrared can enhance many operations effectively.
2, Are Infrared Sensors Dangerous?
Like any technology, infrared sensors can pose risks if misused. However, there have been no reported injuries from exposure to infrared sensors, indicating that they are generally safe and reliable. It’s still wise to use caution when handling any technology.
3, Can You Operate IR Sensors In the Dark?
Infrared sensors are fully operational in the dark, which is why PIR motion sensors can detect movement at night. Just because infrared energy is invisible does not mean it isn't present or detectable in low-light conditions.
Final Thoughts
This overview focuses on infrared sensors, commonly used in wireless technology for detecting surrounding objects and enabling remote control functions. The key features of these sensors include motion and heat detection. Notably, the infrared spectrum is invisible to the human eye.
This article is from JMBom Electronics which offer electronic components, semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes, transistors, ICs, and resistors. For more product information, please go to the website to get it.
Frequently Ask Questions
What Are IR Sensors Used For?
Infrared (IR) sensors are commonly used in motion detection systems. You’ll often find them in lighting controls that automatically switch on lights when someone enters a room, or in security systems to detect intruders. These sensors pick up infrared radiation (heat) changes within a specific area, usually caused by moving people or animals.
What Activates an IR Sensor?
IR sensors are usually triggered by heat, especially from warm-blooded creatures like people or pets. When something warm moves within the sensor’s detection range, it activates the sensor.
What Does an IR Blaster Do?
An IR blaster is a device that allows remote controls to send commands to infrared-controlled electronics. It can also bridge different types of remotes—for example, letting Bluetooth or RF-based remotes control devices that normally require line-of-sight infrared signals.
Can IR Sensors Detect Human Presence?
Yes, IR sensors can detect people. For example, thermal infrared sensors like 32x32 thermopile arrays can detect how many people are in a room based on their body heat. This makes them useful in smart HVAC systems for occupancy detection and energy savings.
Is It Possible to Block an IR Sensor?
Yes, infrared sensors can be blocked by electrically conductive materials. For example, aluminum foil is very effective at blocking infrared radiation because of its high conductivity.
What Is the Detection Range of an IR Sensor?
Typical IR sensors can detect objects up to about 1.25 meters away. The detection range depends on the strength of the infrared beam—longer distances may require a more powerful IR emitter to remain effective.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













