

What is Supercapacitor?
Supercapacitor
In addition to capacitors and batteries, supercapacitors are also known as ultracapacitors or electrochemical capacitors. Due to their high power density, fast charging, and long cycle life, they are ideal for applications that require rapid energy bursts. Unlike conventional batteries, supercapacitors release energy faster and are more durable because they store energy electrostatically rather than chemically. From renewable energy systems to electric vehicles and consumer electronics, their versatility makes them useful in a variety of applications. Supercapacitors are discussed here in terms of their types, working principles, and diverse applications. Moreover, you can also check out: CBB61 Capacitors.
What is a Supercapacitor?
Unlike traditional capacitors and batteries, supercapacitors are advanced energy storage devices. As opposed to batteries, which require chemical reactions to store energy, it stores energy electrostatically, allowing rapid charging and discharging. A supercapacitor is able to deliver a greater amount of power than a battery in a shorter amount of time because of its increased power density. In comparison to batteries, they typically store less energy because they are designed for short bursts of high power rather than long-term storage. In electric vehicles, for backup power supplies, and in renewable energy systems, they are ideal for applications requiring fast energy delivery.
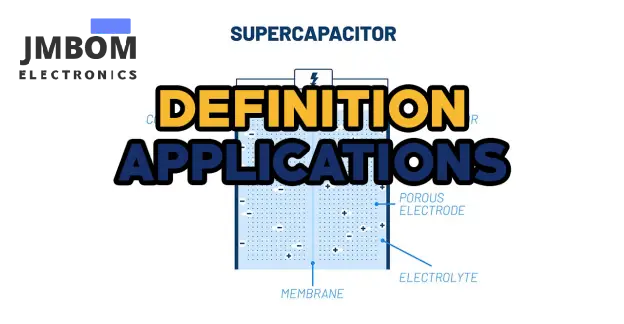
The energy storage capacity of supercapacitors is enhanced by their large surface area, which is separated by an electrolyte between two electrodes. Voltage creates an electric field between the electrodes, storing energy that can be discharged and charged quickly. It is often possible for supercapacitors to last hundreds of thousands of cycles without deteriorating over time, which is an advantage over conventional batteries, which wear out over time. In applications that require high reliability and efficiency, supercapacitors are highly valuable due to their durability and quick response time.
Working Principle
Supercapacitors store energy through two main mechanisms: electrostatic double-layer capacitance (EDLC) and electrochemical pseudocapacitance (PC).
- Electrostatic Double-Layer Capacitance (EDLC): This mechanism separates charges in a Helmholtz double layer, preventing charge transfers across the electrode/electrolyte contact. Carbon is the most widely used material for EDLC electrodes, with activated carbon being the most popular due to its low cost, high porosity, and environmental friendliness.
- Electrochemical Pseudocapacitance (PC): This mechanism involves quick and reversible redox processes on the electrode material's surface. The capacitance of PC can be 10–100 times greater than EDLC. Materials used for PC include conducting polymers like polythiophene, polyaniline, polypyrrole, and transition-metal oxides like MnO₂ and RuO₂.
Applications
Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
In electric and hybrid vehicles (EVs and HEVs), supercapacitors deliver high power quickly, making them increasingly popular. They are often integrated with batteries in these vehicles so they can operate more efficiently and perform better. Supercapacitors, for example, are used in regenerative braking systems to capture and store energy generated during braking so it can be released during acceleration, reducing battery strain. The battery's lifespan is extended and the vehicle's energy efficiency is improved. Also, supercapacitors provide rapid power bursts in situations where rapid power delivery is important, such as when starting and accelerating a vehicle.
Renewable Energy Systems
Solar and wind power systems rely upon supercapacitors to store energy and stabilize power. As a result of changing weather conditions, these systems can produce varying amounts of energy. Supercapacitors reduce power supply fluctuations by storing excess energy generated during peak production times and releasing it at low supply times. These batteries are perfect for handling sudden surges or drops in power due to their fast charging and discharging capabilities. As an example, supercapacitors protect wind turbines from damage and optimize energy output during gusty winds by adjusting blade pitch quickly.
Backup Power and Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
When power outages or voltage drops occur, supercapacitors play a crucial role in ensuring the continued operation of critical devices and systems. The use of supercapacitors ensures uninterrupted operation of sensitive equipment in data centers, hospitals, and industrial facilities. In the event of a blackout or voltage fluctuation, supercapacitors can instantly deliver power, preventing data loss or malfunctioning. It is particularly useful when the power goes out for even a moment.
Consumer Electronics
When fast charging or high-power bursts are required in consumer electronics, supercapacitors are used to boost performance. A supercapacitor can provide a quick burst of power, for example, to improve startup times or extend battery life in items such as cameras, smartphones, and wearable technology. During power transitions or when a device is unexpectedly switched off, they maintain data in devices such as DVRs, laptops, and gaming consoles. Designed for fast-paced consumer applications, these batteries can charge within seconds and withstand thousands of cycles without degradation.
Public Transportation Systems
It is common to see supercapacitors in public transportation systems, particularly electric buses, trams, and trains. As in electric vehicles, supercapacitors store and release energy when the vehicle brakes and accelerates. The result is reduced energy consumption and an increase in efficiency and environmental friendliness in public transportation. The primary energy storage system of some electric buses is the supercapacitor, which allows them to charge quickly at stops and release energy during travel. By utilizing this rapid charging capability, public transit systems are able to reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency.
Smart Grid and Energy Storage Systems
Electricity demand and supply can be managed more efficiently with the help of supercapacitors in smart grid applications. They absorb excess energy and release it during peak demand to stabilize grids, regulate frequencies, and level loads. Combined with batteries, supercapacitors provide rapid power delivery in energy storage systems. Modern electrical grids are more reliable and stable due to their fast response time and ability to withstand many charge-discharge cycles.
Aerospace and Defense
A supercapacitor's reliability, durability, and capability to operate in extreme conditions make it a popular component in aerospace and defense applications. A rocket engine, wing flaps, and emergency systems require rapid bursts of energy to start. The use of supercapacitors also ensures that critical systems remain operational if primary power fails. High power and fast response time are essential for military missions using supercapacitors in radar systems, missile guidance, and portable devices.
Industrial Equipment and Machinery
In systems that require frequent power cycling or peak power demands, supercapacitors are integrated into industrial equipment and machinery to enhance performance. These batteries are used in cranes, forklifts, and other heavy equipment to lift and move heavy loads in short bursts. Power surges and voltage drops caused by large industrial machines can also be stabilized by supercapacitors. They are ideal for improving industrial operations' efficiency and reliability, reducing battery and electrical component wear through their ability to supply high power in a short period of time.
Medical Devices
There are many applications for supercapacitors in the medical field, including life-saving equipment and portable medical devices. When a patient suffers a cardiac arrest, a defibrillator is used to restore his or her heart rhythm. When a patient's heart beats normally, they release a burst of energy. Wearable medical devices, portable diagnostic tools, and drug delivery systems also rely on supercapacitors. Medical applications require energy storage solutions that can be charged quickly and tolerate frequent use without losing capacity.
Wearable Technology and IoT Devices
Supercapacitors are finding more applications in wearable technology and the Internet of Things (IoT). Sensors and communication modules require quick bursts of energy from supercapacitors in smartwatches, fitness trackers, and health monitors. With supercapacitors, IoT devices can charge faster and operate for a longer period of time, reducing the need for frequent battery replacements. The power sources they use are usually small and energy-efficient. Because of their high power density and long cycle life, they are suitable for long-term operation and continuous operation.
Advantages
- High Power Density: Supercapacitors can deliver high power bursts in a short amount of time. They can reach a power density of up to 15 kW/kg, and some customised composite electrodes have achieved a maximum power density of 990 kW/kg.
- Fast Charging and Discharging: Supercapacitors can be fully charged in just a few seconds (∼30 s), making them ideal for applications requiring rapid energy bursts or quick recovery of energy.
- Long Cycle Life: Supercapacitors can endure from hundreds of thousands to several million cycles with minimal degradation in performance. This is vastly superior to traditional batteries, which typically last for thousands to tens of thousands of cycles.
- Environmental Friendliness: Supercapacitors are readily biodegradable and their waste components are simple to dispose of because they are primarily composed of carbon and its compounds.
Faqs
What is the difference between a capacitor and supercapacitor?
As opposed to a regular capacitor, a supercapacitor has a very high capacitance, also known as an ultracapacitor. Electrochemical reactions store energy through an electrochemical reaction, whereas capacitors store energy through static charges.
What are the components of a supercapacitor?
Active components of the supercapacitor are electrodes and electrolytes, whereas passive components are others. In general, supercapacitors consist of two electrodes or current collectors separated by electrolyte or separators.
Are supercapacitors AC or DC?
DC power is required for their operation as energy storage devices. Carbon-based electrodes with EDLC-type supercapacitors typically have a complex microporous structure, which leads to large electrochemical resistance and high charging and discharge frequencies.
Wrapping Up
Throughout many industries, supercapacitors have become a crucial technology because they can store and deliver energy quickly. In applications where quick energy bursts and long cycle life are essential, they are indispensable due to their fast charging, high power density, and exceptional durability. A supercapacitor's power storage capabilities range from boosting the performance of consumer electronics to enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems.
The aerospace, defense, medical device, and smart grid sectors are also driving innovation. Providing a powerful, long-lasting, and energy-efficient alternative to traditional batteries and capacitors, supercapacitors will continue to play a key role as industries move towards greener, more sustainable energy solutions. They play a crucial role in advancing next-generation solutions and systems across a wide range of industries.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













