

2SA1015 Transistor: Pinout, Features, and Common Uses
Catalog
What is the 2SA1015 Transistor?Pin ConfigurationFeatures and Specifications of the 2SA1015 TransistorReplacements and Equivalents for the 2SA1015 TransistorHow to Use a 2SA1015 Transistor (with Circuit Diagram)Applications of the 2SA1015 TransistorFrequently Ask QuestionsThe 2SA1015 is a low-frequency PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT), primarily used in amplification circuits. It features a semiconductor structure with an N-type layer sandwiched between two P-type layers. This transistor is commonly found in a TO-92 package.
Note on Marking:
In some cases, the prefix "2S" on the 2SA1015 transistor may be omitted from the physical package, so it may simply be labeled as A1015.
This article provides a complete overview of the 2SA1015 transistor, covering its pinout, key features, technical specifications, working principle, and typical applications.
What is the 2SA1015 Transistor?
The 2SA1015 is a PNP-type bipolar junction transistor (BJT) with three standard terminals: emitter, base, and collector. It is primarily intended for general-purpose amplification. In this PNP transistor, the N-type layer functions as the base, while the two P-type layers form the emitter and collector.
In a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), the base terminal is always more negative than the emitter, especially in a PNP configuration. This allows conduction through both majority and minority charge carriers—holes and electrons. For PNP transistors, holes are the majority carriers.
When a negative voltage is applied to the base, the transistor becomes forward-biased, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. The 2SA1015 operates as a current-controlled device, where a small current at the base controls a much larger current flowing between the emitter and collector.
In this type of transistor, the P-type emitter is connected to a positive voltage (+), while the N-type base is connected to a negative voltage (−). Current flows only when the base is at a lower potential than the emitter.
Additionally, the 2SA1015 transistor is classified into four groups based on its DC current gain (hFE): O, Y, G, and L. Each group represents a different gain range:
- O: 140
- Y: 240
- G: 400
- L: 700
The amplification factor is typically expressed as the DC current gain, which can be calculated using the following formula:
Gain (hFE) = IC / IB
In this formula, IC is the collector current, and IB is the base current.
Pin Configuration
The pinout of the 2SA1015 transistor is shown below. It has three terminals, each serving a specific function
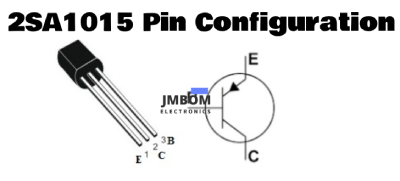
2SA1015 Pin Configuration
- Pin 1 (Emitter): Allows current to flow into the transistor from this terminal.
- Pin 2 (Collector): Current flows out through this terminal.
- Pin 3 (Base): Controls the current flow between the emitter and collector.
Features and Specifications of the 2SA1015 Transistor
- Transistor Type: PNP
- Package Type: TO-92
- Power Dissipation: 0.4 W (400 mW)
- DC Current Gain (hFE): Up to 400
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (V<sub>CEO</sub>): -50 V
- Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (V<sub>CBO</sub>): -50 V
- Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (V<sub>EBO</sub>): -5 V
- Collector Current (I<sub>C</sub>): 150 mA (0.15 A)
- Collector Dissipation: 400 mW
- Saturation Voltage (V<sub>CE(sat)</sub>): 0.3 V (typical)
- Saturation Voltage (V<sub>EB(sat)</sub>): 1.1 V
- Base-Emitter Voltage (V<sub>BE</sub>): 1.45 V DC
- Transition Frequency (f<sub>T</sub>): 80 MHz
- Noise Figure: 1 dB
- Material: Molded plastic case
- Operating and Storage Temperature Range: –55°C to +150°C
Replacements and Equivalents for the 2SA1015 Transistor
- Direct Replacements / Alternatives: 2SA1013, KST93, 1275, KSA1013, KTA1275
- SMD (Surface Mount) Equivalent: LT1-BA or 2SA1015 in SOT-23 package
- Complementary Transistor: 2SC2383 (NPN type, commonly paired with 2SA1015 in push-pull configurations)
- Equivalent Transistors: 2SA495, 2SA561, 2SA564A, 2SA573, 2SA675, 2SA705, 2SA781, 2SA850, 2SA999 BC257, BC307, BC557, BC558, BC559, BC212 NTE290A, 2N3494, KTA1015, KT3108A
How to Use a 2SA1015 Transistor (with Circuit Diagram)
The following is a simple LED flasher circuit that demonstrates how the 2SA1015 transistor can be used. In this circuit, the transistor plays a central role in switching the LED on and off.
Required Components:
- 2SA1015 PNP transistor (used in a Darlington pair)
- Capacitors: C1 = 200 µF, C2 = 1 µF
- Resistors: R1 = 2 MΩ, R2 = 200 Ω
- Power supply: 3V battery
- LED
- (Optional) Additional transistor for Darlington configuration
The 2SA1015, when paired with another transistor in a Darlington configuration, amplifies the current enough to flash the LED. The capacitor and resistor values control the timing cycle of the flashing.
In the above circuit, R1 and C1 form a timing network that generates pulses and controls the switching of the first transistor (Q1). This transistor, in turn, acts as a switch to control the second transistor (Q2), which is primarily used to increase current flow to drive the LED.
Initially, Q1 conducts, allowing current to flow through C1, R2, and the LED. This continues until the voltage across C1 rises above a certain level. At that point, Q2 starts conducting, allowing current to flow through the LED, turning it ON.
After a set time, C1 discharges through R1, which reduces the voltage at the base of Q1, causing Q1 to turn off. As a result, Q2 also turns off, and the LED switches OFF. The capacitor C1 then begins to charge again, and the cycle repeats.
This continuous charge-discharge cycle creates a blinking effect, making the LED flash repeatedly.
Applications of the 2SA1015 Transistor
The 2SA1015 transistor is commonly used in a wide range of low-power applications, particularly in audio and signal amplification. Some of its typical uses include:
- Audio Frequency (AF) Amplifiers – Ideal for general-purpose audio signal amplification.
- Switching Applications – Functions effectively as a PNP switch in low-voltage circuits.
- LED Flasher Circuits – Used in timing and blinking light circuits.
- Driver Stages in Amplifier Circuits – Often used in the driver stage of power amplifiers.
- Darlington Pair Configuration – Can be paired with another transistor for higher current gain.
- Voltage and Power Amplification – Widely used for amplifying both voltage and current signals.
- Complementary Pairing with NPN Transistors – When paired with an NPN transistor (e.g., 2SC2383), it creates a balanced complementary circuit ideal for push-pull configurations.
This wraps up an overview of the 2SA1015 transistor, covering its pinout, features, specifications, working principle, and practical applications.
Note: Pin configuration may vary slightly depending on the manufacturer, so it's always a good idea to check the datasheet before using the transistor in your circuit.
Key Insight: While PNP and NPN transistors perform similar functions, their current flow and voltage polarity are opposite. In a PNP transistor like the 2SA1015, current flows from emitter to collector, and the base must be more negative than the emitter for conduction to occur.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is equivalent to a 2SA1015 transistor?
Equivalent transistors for the 2SA1015 include:
2SA495, 2SA564A, 2SA675, 2SA561, NTE290A, 2SA850, BC257, BC307, BC557, 2SA999, 2SA705, BC558, 2SA781, BC559, BC212, 2SA573, 2N3494, KTA1015, and KT3108A.
What does a 2N2222 transistor do?
The 2N2222 is a popular NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) widely used for low-power amplification and switching. It supports low to medium current and voltage levels and can operate at moderately high speeds, making it suitable for general-purpose applications.
What is the A1015 transistor used for?
The A1015 transistor is commonly used in audio amplifier circuits, such as audio preamplifiers and amplifier stages. It helps improve the clarity and strength of audio signals, making it suitable for devices like radios, MP3 players, and doorbells.
What is the equivalent of a 2N5551 transistor?
The complementary transistor to the 2N5551 is the 2N5401. Equivalent alternatives include 2N5551K, BC637, NTE194, BC639, 2N5833, BC487, and 2N5551G. The 2N5550 is also a similar transistor.
What transistor is similar to the 2N2222?
Transistors similar to the 2N2222 include 2N3904, BC547, BC548, and 2N3906.
How much voltage can a 2N2222 transistor handle?
The 2N2222 can safely operate within its maximum ratings without overheating or damage. The base-emitter trigger voltage is around 200 mV, and the maximum allowable base current is approximately 200 mA.
What is the equivalent of the 2SC2383 transistor?
The Toshiba 2SC2383-Y (T6DNS, FM) transistor has been declared obsolete. However, the Onsemi KSC2383YTA (part number KSC2383YTACT-ND) is a suitable replacement.
What type of transistor is the 2SC5200?
The 2SC5200 is an NPN transistor.
- Maximum Collector Current (Ic): 15 A
- Maximum Collector-Emitter Breakdown Voltage (Vce): 230 V
- Saturation Voltage (Vce(sat)) at Ib and Ic: Around 3 V at 800 mA and 8 A
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













