
NTE159M Transistor: Overview, Pinout & Common Uses
Catalog
What Is the NTE159M Transistor?How the NTE159M Transistor WorksPin Configuration of NTE159M TransistorFeatures and SpecificationsSMD Equivalents of NTE159M TransistorHow to Use the NTE159M Transistor – Circuit ExampleWhere to Use the NTE159M Transistor – ApplicationsIn ConclusionIndustry-standard transistors such as the NTE123A and NTE159M are commonly used across a range of electronic applications. The NTE123A is an NPN transistor, while the NTE159M is a PNP type. Both come in a TO-18 metal can package, making them suitable for use in audio amplification, moderate-speed switching, and other circuits. The NTE159M can function either as a switch or an amplifier depending on the design requirements.
When functioning as an amplifier, the NTE159M transistor operates in the active region. In switching applications, it works between the cutoff and saturation regions. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the NTE159M transistor, including its pin layout, key features, technical specifications, and typical applications.
What Is the NTE159M Transistor?
The NTE159M is a general-purpose PNP transistor housed in a TO-18 metal can package. Its complementary NPN counterpart is the NTE123A. This transistor offers a maximum DC current gain (hFE) of up to 300 and can handle collector currents up to 600mA. With a low collector-emitter saturation voltage—typically under 1V—it is well-suited for use in both amplification and switching circuits.
PNP and NPN transistors can be paired together to form a complementary set, making them ideal for circuits that require both types—such as H-bridge configurations, push-pull stages, and Class B amplifiers. As an alternative to the NTE159M, the 2N2907 transistor can be used, which comes in the more common TO-92 plastic package.

The NTE159M is a PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) consisting of three semiconductor layers arranged in a P–N–P structure, with the N-type material (the base) sandwiched between two P-type regions (the emitter and collector). In this configuration, the base terminal is negatively biased relative to the emitter, which is required for the transistor to operate properly.
As a PNP BJT, conduction occurs via both electrons and holes, although holes are the majority charge carriers responsible for current flow in this type of transistor.
How the NTE159M Transistor Works
The operation of a PNP transistor like the NTE159M is generally similar to that of an NPN transistor, with key differences in voltage polarity and current direction. In a PNP transistor, the base is negative relative to the emitter, while in an NPN transistor, the base is positive.
Both types are classified as current-controlled devices, meaning a small current at the base terminal controls a much larger current flowing through the emitter and collector terminals.
In a PNP transistor, when a suitable negative voltage is applied to the base, the transistor becomes forward-biased, allowing hole flow (the majority charge carriers) from the emitter to the collector. In contrast, an NPN transistor conducts primarily through electrons, with current flowing from collector to emitter.
Pin Configuration of NTE159M Transistor
The NTE159M transistor has three pins, each serving a specific function:
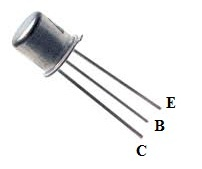
NTE159M Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin 1 (Base): Controls the transistor's biasing. It is responsible for turning the transistor ON or OFF.
- Pin 2 (Collector): Allows current to flow through the transistor and is typically connected to the load.
- Pin 3 (Emitter): Serves as the path for current to exit the transistor and is usually connected to ground.
Features and Specifications
The key features and electrical specifications of the NTE159M transistor are as follows:
- Type: PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT)
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 100 to 300
- Collector Current (IC): Continuous up to 600 mA
- Collector–Emitter Voltage (VCE): 60 V
- Collector–Base Voltage (VCB): 60 V
- Emitter–Base Voltage (VBE): 5 V
- Package Type: TO-18 metal can
- Maximum Collector Current: –0.6 A
- Collector Power Dissipation (PC): 0.4 W
- Transition Frequency (fT): 200 MHz
- Operating and Storage Temperature Range: –65°C to +200°C
- Configuration: Common base
- Package Diameter: 5.84 mm
- Height: 5.33 mm
- Total Power Dissipation: 0.4 W
- Dimensions: 5.84 mm (diameter) × 5.33 mm (height)
- Number of Terminals: 3
- Number of Elements per Chip: 1
- Material: Silicon (Si)
- Mounting Type: Through-hole
- Complementary Transistor: NTE123A (NPN)
- Equivalent / Replacement: 2N2907A (TO-92 package)
SMD Equivalents of NTE159M Transistor
Several surface-mount (SMD) versions are available as functional equivalents to the NTE159M transistor. These alternatives offer the same or similar electrical characteristics in compact, modern SMD packages:
- SOT-223: DZT2907A, PZTA55
- SOT-23: FMMT2907A, FMMT2907AR, KN2907AS, FMMTA55, KST55, KST2907A, MMBTA55, PMBT2907A, SMBTA55, PMST2907A, KTN2907AS
- SOT-89: DXT2907A
- SOT-323: KTN2907AU, FJX2907A, MMST2907A
These SMD versions are ideal for compact PCB designs where through-hole components like the TO-18 package are not suitable.
How to Use the NTE159M Transistor – Circuit Example
A practical application of the NTE159M transistor is in a blown fuse indicator circuit, as illustrated below. The components required to build this circuit include:
- NTE159M PNP bipolar junction transistor (Q1)
- 1N4148 or 1N4001 diode (D1)
- Red LED
- Resistors: 510 ohms (R1) and 510k ohms (R2)
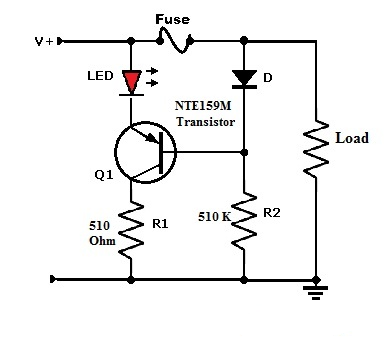
Blown Fuse Indicator Circuit using NTE159M Transistor
This circuit is designed to provide a visual alert—via the red LED—when a fuse has blown in an electrical system. It’s particularly useful in automotive or motorcycle electrical systems, where identifying a blown fuse early can help prevent further damage or troubleshooting complexity.
When the fuse is intact, the transistor remains OFF and the LED stays dark. If the fuse blows, the transistor becomes forward biased, allowing current to flow and illuminating the LED. This simple yet effective circuit helps users quickly pinpoint faults in the system, making maintenance and repairs faster and more efficient.
In this circuit, the NTE159M PNP transistor plays a crucial role by functioning as an electronic switch. When the fuse is intact and operating normally, the voltage at the transistor's base is approximately –0.7V. In this condition, the transistor remains in the cutoff region, meaning it does not conduct. As a result, the red LED stays off, indicating everything is functioning properly.
However, if the fuse blows, current can no longer flow through it. This causes the voltage at the transistor’s base to drop to 0V. In response, the transistor enters the saturation region, allowing current to flow from the emitter to the collector. This activates the LED, which lights up to signal that a fault has occurred in the system.
In a typical car's electrical system, there are multiple types of fuses protecting different circuits. By connecting this blown fuse indicator circuit in parallel with each fuse, you can easily monitor the status of each one. This circuit is particularly useful in applications such as car radios, battery-powered systems, toys, and other low-voltage electronics, helping users quickly identify and respond to blown fuses.
Where to Use the NTE159M Transistor – Applications
The NTE159M PNP transistor is versatile and suitable for a wide range of general-purpose applications, including:
- Switching operations, especially at medium speeds
- High-frequency amplifier circuits
- Class B amplifier designs
- Push-pull amplifier stages
- H-bridge motor control circuits
- General-purpose switching and amplification
- Complementary pair circuits, when paired with its NPN counterpart (e.g., NTE123A), for use in H-bridges, Class B and push-pull amplifiers
- Darlington pair configurations for higher current gain
- Low-power amplification in battery-operated devices
- Simple electronic projects, such as dual-LED blinkers, siren circuits, and lamp flashers
Thanks to its reliable performance and compatibility with common NPN transistors, the NTE159M is a preferred choice in both analog and digital electronics.
In Conclusion
The 2N2907 is a PNP-type bipolar junction transistor commonly used in low-power applications and switching-based amplifier circuits. It operates efficiently at moderate temperatures and is capable of high-speed switching.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













