

What is a Hard Disk Drive?
Catalog
What is a Hard Disk Drive?Description of a Hard Disk Drive Computers Require Hard Disks for Reasons:How do Hard Disk Drives Work?3 Benefits of Using HDD for Data StorageFrequently Asked QuestionsWhat is a Hard Disk Drive?
A hard disk drive (HDD), also known as a hard drive, is a type of storage medium that retains data even when the power is off, making it non-volatile. It's an essential component in all computer systems, serving as a repository for operating systems, applications, and various files through the use of magnetic platters.
HDDs are typically found within the casing of desktops, laptops, and a variety of other devices, including mobile gadgets and large-scale data storage solutions in corporate settings. These drives facilitate the process of accessing and recording information on their magnetic surfaces.
In more detail, HDDs manage the input and output operations of data on their disks, functioning as either the main or auxiliary storage in a computer system. They are typically located in a designated drive bay and interface with the computer's motherboard using various connection types such as Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA), Serial ATA, parallel ATA, or Small Computer System Interface (SCSI) cables. Additionally, they draw power from a power supply unit and are capable of retaining data even when the system is not powered.
While the terms "hard disk drive" and "hard disk" are not identical, they are often used interchangeably to describe the combined unit of the drive and its packaging.

What is a hard disk drive?
Description of a Hard Disk Drive
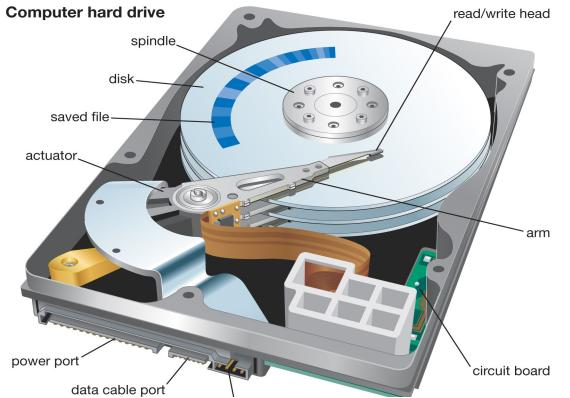
A hard disk drive is encased in a sturdy metal enclosure to protect its sensitive internal components from damage during regular operation. The exterior of the hard drive resembles a compact metal box, often marked with indications that it is a hard disk drive or HDD.
Upon removing the metal casing of an internal HDD, you are presented with the intricate inner workings. The most noticeable features are the rotating platters and the actuator arm. These components operate to access and record data as required. The platters spin at high speeds, and the actuator arm, which extends over the platters, moves to position the read/write head precisely over the data tracks on the platters.

An inner picture of a hard disk drive
Computers Require Hard Disks for Reasons:
1. Non-Volatile Storage: Hard disk drives (HDDs) offer non-volatile storage, meaning they retain data even when the power is off. This is essential for saving and accessing data, applications, and operating systems that need to be available after reboots.
2. Operating System and Application Hosting: HDDs serve as the primary medium for installing and running operating systems and various software applications. These are the programs that enable users to interact with the computer and perform tasks.
3. Document and File Preservation: Users rely on hard disks to save documents, files, and other data that they want to keep. This data preservation is crucial for personal and professional use, allowing for long-term data management.
4. Data Accessibility: Hard disks allow users to access stored data quickly and efficiently. This is important for productivity and the overall user experience, as it enables the retrieval of files and information without delay.
5. Data Persistence: HDDs ensure that data is not lost when the computer is powered down, which is a necessity for any data that needs to be preserved over time.
6. System Performance: While not directly related to storage, the speed and capacity of hard disks can impact a computer's performance. Faster hard drives can lead to quicker boot times and application loading.
How do Hard Disk Drives Work?
Hard disk drives function through a series of components. At their core, they are made up of multiple disk platters, which are circular disks crafted from materials like aluminum, glass, or ceramic. These platters are housed within an enclosed space and are arranged around a central spindle.The motor, connected to the spindle, enables them to spin at rapid velocities.Within this sealed environment, there are also read/write heads that use magnetic fields to store and retrieve data on tracks located on the platters, facilitated by a magnetic head. The platters have a thin film of magnetic substance applied to their surface.The platters can be driven by the motor to rotate at velocities as high as 15,000 revolutions per minute.While the platters are in motion, another motor is responsible for the precise positioning of the read and write heads. These heads are crucial for magnetically recording and accessing information on each platter.
a hard disk drive
3 Benefits of Using HDD for Data Storage
1. Cost-Effectiveness of HDDs
HDDs offer a more budget-friendly option when compared to other storage solutions. They are significantly less expensive than SSDs with equivalent storage capacities, such as the SAS-3Gbps HDD. The lower production costs of HDDs, calculated on a per megabyte basis, make them a more economical choice in terms of price.
2. Wide Availability of HDDs
HDDs have been in production for a long time, making them more readily available in the market. Whether you're looking for an external or internal hard drive, you're likely to find an HDD in most tech stores. The market presence of HDDs, especially those with SATA or SAS interfaces like the SAS-3Gbps HDD, has been more established than that of SSDs, despite the growing demand for SSDs. Unless there's a dramatic increase in SSD production, HDDs will continue to be a popular choice for those looking to upgrade their PCs.
3. Higher Storage Capacity of HDDs
HDDs typically come with larger base storage capacities, with a standard size of 500 GB being common in the market, which is more than half of what you'd find as the starting capacity for SSDs. Newer models of HDDs also boast even greater storage capacities than their predecessors. This means you can store a substantial amount of data on a single HDD. It's not uncommon to find external hard drives with capacities as large as 6 TB.

3 Benefits of using HDD
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a hard disk drive?
HDDs, as a form of non-volatile storage, preserve data when the computer is powered down, thus frequently being selected for extended data retention.
2. Are HDDs or SSDs better?
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are generally preferred over Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) due to their superior performance, including quicker data access times, lower power usage, and the absence of moving parts, which can lead to greater reliability and durability.
3. How big of a hard drive do I need?
The size of the hard drive you need depends on your storage requirements. However, 1TB or 2TB drives are popular choices and offer a good balance between cost and capacity for most users.
4. How long does a hard drive typically last?
The typical lifespan of a hard disk drive (HDD) is three to five years before a component might fail. This doesn't always mean the drive is beyond repair, but it's a general estimate of how long they can be expected to last, regardless of whether they are used in servers, desktops, or as external drives.
5. What are the drawbacks of hard disk drives?
HDDs have several disadvantages, including slower performance with large files, higher power consumption, heat generation due to moving parts, and less durability, especially when used in portable devices.
6. What is the distinction between an external hard drive and a portable hard drive?
External hard drives are usually bulkier and heavier than portable ones and often need a power supply and a USB link for data transfer.Portable hard drives are more compact and may not need an external power source, making them more convenient for on-the-go use.
7. Do I need both SSD and HDD?
Using both an SSD and an HDD can provide benefits.An SSD offers advantages such as low power consumption and fast loading speeds, making it ideal for the operating system and frequently used applications. Many users choose to pair an SSD with an HDD to take advantage of the larger storage capacity and lower cost per gigabyte that HDDs provide.
JMBom Electronics, a company that collaborates with various manufacturers, supplies a broad array of electronic components. Their product lineup includes semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes, integrated circuits (ICs), and resistors. This article has been brought to you by JMBom Electronics. Should you seek further details regarding their products, please visit their website.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













