
Guide to Time Delay Relay
Catalog
What is a Time Delay Relay?How Does a Time Delay Relay Work?Different Types of Time Delay Relays Practical Applications of Time Delay Relays Frequently Asked QuestionsRelated ArticlesWhat is a Time Delay Relay?
A Time Delay Relay (TDR) is a type of relay that incorporates an intrinsic time-delay mechanism. This implies that upon activation, the relay does not respond instantly. Rather, it pauses for a pre-determined duration before executing its function. Such relays are particularly beneficial in scenarios where a pause prior to activation is necessary, like in industrial automation or security systems. The time-delay relay may feature adjustable timing or be set with a static delay. Certain relays offer a variety of time-range settings, while others confine users to a specific range.


Time Delay Relay
How Does a Time Delay Relay Work?
A Time Delay Relay (TDR) functions by regulating the timing of its contacts, either postponing their opening or closing following a specific triggering event.The main function of a TDR is to manage the time gap between the introduction of a stimulus and the following reaction.This precise timing capability is vital across various electrical and industrial applications.
Inside a TDR lies an internal timing mechanism, which can be digital, pneumatically-driven, or mechanical in nature. Upon receiving an initiating signal, the timing system begins counting down according to the preset delay duration. This delay can range from nanoseconds to several minutes, depending on the design and specific application needs.
The relay contacts, which are essential for opening or closing the circuit, will only change state after the delay period has elapsed. For instance, in a normally open TDR, the contacts will remain open until the delay period ends, at which point they will close to complete the circuit. On the other hand, in a normally closed TDR, the contacts will stay closed until the delay time concludes, causing them to open and interrupt the circuit.
The delay time is typically adjustable, allowing users to fine-tune the timing to fit specific requirements. This adjustment can be made using dials, digital interfaces, or software, depending on the type of TDR being utilized. Moreover, some TDRs offer multiple timing functions, such as on-delay and off-delay, providing additional flexibility in their operation.
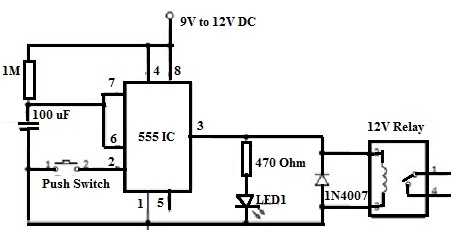

Time Delay Relays Circuit
Different Types of Time Delay Relays
1. Delayed-On Timer Relays
Delayed-on timer relays are the most prevalent variety. Upon receiving the control signal, these relays wait for a set delay period before actuating the output. They are widely utilized in scenarios that necessitate a time lag before initiating an action, such as in motor control circuits.
2. Delayed-Off Timer Relays
Delayed-off timer relays operate in contrast to delayed-on timers. Once the control signal is withdrawn, these relays keep the output active for a specified duration before deactivating. They are employed in situations where an action needs to be sustained for a certain period after the control signal is discontinued.
3. Pulse Timer Relays
Pulse timer relays provide a single output pulse of a predetermined duration upon activation. These relays are beneficial in applications that require a fleeting action, such as in industrial automation systems where a single pulse can set off a sequence of operations.
4. Recurring Timer Relays
Recurring timer relays alternate between on and off states for set periods, creating a repeating cycle. They are ideal for applications that demand periodic operations, such as in blinking lights or rhythmic control systems.
5. Versatile Timer Relays
Versatile timer relays offer multiple timing functions within a single device, providing adaptability for various applications. Capable of being configured for delayed-on, delayed-off, pulse, and recurring operations, these relays are well-suited for complex control systems.
6. Phase Sequence Timer Relays
Phase sequence timer relays are specifically designed for motor starting applications. They manage the transition from star connection to delta configuration in electric motor windings, reducing the starting current and ensuring a smooth motor start.

Different Types of Time Delay Relays
Practical Applications of Time Delay Relays
1. Industrial Automation:
Time Delay Relays are utilized to manage the sequential starting and stopping of conveyor systems for the smooth processing of materials, as well as to regulate the timing of various machine functions, such as initiating motors, triggering electromagnets, and governing actuators.
2. Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) Systems:
Time Delay Relays prevent premature cycling by creating a lag between successive starts of the HVAC compressor, and they manage the delay in the activation or deactivation of fans to maintain adequate air circulation and temperature management.
3. Lighting Control:
Time Delay Relays guarantee that lighting stays illuminated for a designated time after being switched on, offering ample light for emergency exits, and they regulate the duration that emergency lighting remains active during power outages, ensuring safety and adherence to regulatory standards.
4. Automotive Applications:
Time Delay Relays oversee the intermittent functioning of windshield wipers to enhance visibility during light rainfall and regulate the operation duration of rear defoggers, ensuring clear visibility while minimizing power usage.
5. Security Systems:
Time Delay Relays incorporate a delay before activating an alarm, permitting authorized individuals to deactivate the system, and they manage the timing for the locking and unlocking of doors and access control systems to maintain security and restricted access.
6. Household Appliances:
Time Delay Relays handle the timing for various washing cycles in washing machines for optimal performance and control the length of cooking and defrosting cycles in microwaves, offering accurate timing for a variety of functions.


Applications of Time Delay Relays
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Definition of a Time Delay Relay:
Time Delay Relays, also known as interval timers, are used to manage the duration for which an electrical load receives power. They are alternately named pulse shaping timers, bypass timing timers, interval delay timers, and delay on energization with instantaneous transfer timers.
2. Purpose of Timer Relays:
Precise Timing: Timer relays permit the setting of exact time intervals, thereby governing various operations. Delay Options: They provide versatility by accommodating both delay-on and delay-off functionalities.
3. Operation of Time Delay Switches:
Upon the application of power to the coil, the ON DELAY timing cycle initiates, and the contacts do not change state at this stage. Once the ON DELAY period concludes, the contacts shift state, either making (in the case of normally open contacts) or breaking (in the case of normally closed contacts) the circuit with the load.
4. Distinction Between Timer Relays and Regular Relays:
The primary difference between relays and Time Delay Relays lies in the operation of the output contacts in response to the control signal: in a standard relay, the contacts open or close immediately when voltage is applied to or removed from the coil; in Time Delay Relays, the contacts may open or close after a predetermined time delay.
5. Role of Time Delay:
Time delay is the interval a process waits before execution, calculated as the difference between anticipated and actual response times. It is often used synonymously with latency in the field of computer science.
6. Components of a Time Delay Relay:
A Time Delay Relay consists of an electromechanical output relay combined with a control circuit. This control circuit is made up of solid-state components and timing mechanisms that dictate the relay's operation and timing range.
7. Application of Time Delay Relays:
Time Delay Relays are extensively utilized in industrial settings, HVAC systems, and building management to implement time-delayed switching. They are essential for initiating motors, managing electrical loads, or automating processes and play a critical role in achieving specific logical control needs.
8. Principle of Timer Relay Operation:
The working principle of a timer relay is based on electromagnetism. One relay coil is continuously energized, while the other can be activated or deactivated with an electric signal from a control device such as a telephone or computer system. The "on" coil is always powered, ready for immediate activation.
Related Articles
What are Automotive Relays & How it Works
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













