

What Ballast Resistor is and How It works
Catalog
Definition of Ballast ResistorWhat does a Ballast Resistor do?Fundamentals of Ballast ResistorsApplications of a Ballast ResistorBallast Resistor for Automotive ApplicationsBallast Resistor in Fluorescent LampsBallast Resistor in a LED CircuitTypes of Ballast ResistorsFunction and ImportanceHow to Test a Ballast ResistorAdvantagesFrequently Asked QuestionsRelated ArticlesDefinition of Ballast Resistor
A ballast resistor is a special type of resistor that helps control the amount of current in a circuit to prevent it from getting too high. The term "electric ballast" can refer to various devices, like resistors, capacitors, or inductors, that help keep a circuit stable by managing current and voltage levels.
Ballast resistors work by changing their resistance depending on the current flowing through them. If the current goes above a certain limit, the resistance increases; if the current drops, the resistance decreases.
This means the ballast resistor tries to keep a steady current flowing in the circuit.
Unlike a load resistor, which has a fixed resistance no matter what, a ballast resistor can adjust itself based on the current in the system.
These types of resistors are not commonly used anymore because modern electronic circuits can do the same job more effectively.
What does a Ballast Resistor do?
The word "ballast" means something that helps keep things stable, and that is exactly what a ballast resistor does in an electrical circuit.
A ballast resistor is placed in a device to help manage changes and protect the other parts of the circuit.
When the current going through the resistor increases, the temperature goes up as well. This rise in temperature causes the resistance to increase too.
So, when the resistance goes up, it helps limit the current flowing through the circuit.
Ballast resistors are often found in cars, where they help start the engine. When you turn on the starter motor, the ballast resistor keeps the battery from losing too much voltage.
They are also used in lighting, like with fluorescent lamps, LED lights, and neon signs.
Fundamentals of Ballast Resistors
Ballast resistors are electrical components that help to stabilize an electrical circuit. They are designed to restrict the current passing through a circuit by increasing their resistance as the current grows. This enables them to safeguard other components in the circuit from overcurrent damage.
Ballast resistors are frequently found in devices such as ignition systems, fluorescent lamps, and electronic ballasts. In ignition systems, ballast resistors are used to lower the voltage to the ignition coil once the engine has started, which helps to extend the lifespan of the ignition system components.
The resistance of a ballast resistor is determined by its construction and material. Some ballast resistors are made of wire-wound ceramic or metal film, while others are made of wire-wound or carbon composition. The resistance value of a ballast resistor is typically specified in ohms and can range from a few ohms to several hundred ohms.
Ballast resistors differ from load resistors in that their resistance changes with variations in current. Load resistors, however, have a fixed resistance value and are used to dissipate power in a circuit.
In summary, ballast resistors are crucial components in electronic circuits that help to maintain circuit stability. They limit the current flowing through the circuit and protect other components from overcurrent faults. The resistance of a ballast resistor varies with changes in current, and they are commonly used in ignition systems, fluorescent lamps, and electronic ballasts.
Applications of a Ballast Resistor
A ballast resistor is important for controlling the current and voltage in an electrical system. It helps prevent equipment from facing issues like too much current or too much voltage.
You will mostly find ballast resistors in cars and lighting systems.
Ballast Resistor for Automotive Applications
In a car engine, a ballast resistor is used in the ignition system, and it is often called an ignition ballast resistor.
Typically, this resistor is placed between the main power source of the ignition coil and the coil itself. Its job is to lower the risk of the ignition coil failing.
When the starter motor is cranking the engine, the ignition ballast resistor reduces the voltage and current going to the coil.
This means that lower current results in less heat, which helps the ignition coil last longer.
However, the ignition system still needs a higher voltage that matches the power source. To make this happen, a jumper wire is connected to the ignition ballast resistor. When starting the engine, this wire provides the extra voltage needed for the ignition coil.
Ballast Resistor in Fluorescent Lamps
Fluorescent lighting is a popular and energy-efficient way to light up a space. However, it has a downside. When a fluorescent lamp is connected directly to a voltage source, it can heat up quickly. This happens because the lamp draws a lot of current right when it is turned on. To prevent overheating from this high current, a ballast resistor is used in the circuit, connected in series with the bulb. The main job of the ballast resistor is to reduce the voltage and control the current.
For the lamp to light up, it needs to create an arc between its two electrodes. This requires a high starting voltage, which is roughly equal to the supply voltage. Once the arc is formed, the ballast resistor supplies the necessary voltage during the start-up and then reduces the voltage while managing the current flow. In the diagram below, you can see how a fluorescent light tube is connected to a ballast resistor and a starting switch.
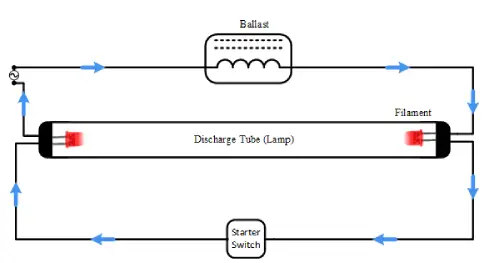
Ballast Resistor in Fluorescent Lamps
Ballast Resistor in a LED Circuit
An LED, or Light Emitting Diode, is a very delicate device that can get damaged if the supply voltage is too high.
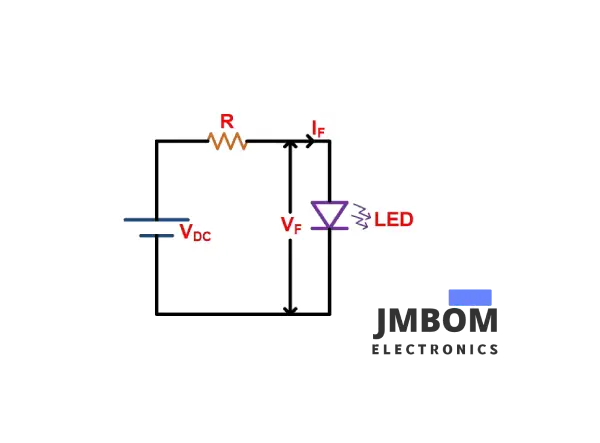
To prevent this, a ballast resistor is added in series with the LED. This resistor helps lower the voltage across the LED to the safe level it needs.
It is important to choose the right value for the ballast resistor. Let’s look at an example.
Ballast Resistor
Imagine you have a single LED connected in series with a power supply that has a higher voltage than what the LED can handle. In this case, you cannot connect it directly without using a resistor.
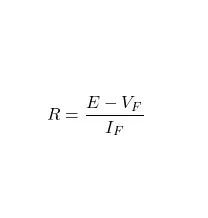
Where:
VF = Forward voltage of the LED
IF = Forward current of the LED
R = Resistance of the ballast resistor
E = Supply voltage
For example, if the DC source value is 5 volts, the forward voltage of the LED is 3.1 volts, and the forward current is 9 milliamps. Now, using the equation above, you can calculate the resistance needed for the ballast resistor.
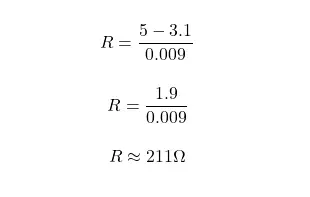
Hence, for this example, you would need to connect a resistor with a value of 211 ohms or higher.
Types of Ballast Resistors
Fixed Ballast Resistor
As the name suggests, the resistance of this type is constant. Fixed ballast resistors are typically used in simple circuits.
These resistors are used in different applications where a high resistance is needed.
For example, you can find them in circuits with neon lamps or LEDs. They are also used in variable-speed fans.
In a variable-speed fan, a fixed ballast resistor with two center taps is used. The fan's selector switch adjusts the resistance using the center tap, and this changes the fan's speed based on the resistance value.
Self-variable Ballast Resistor
This type of resistor can change its resistance when the current changes. When the current flowing through the resistor increases, it raises the temperature of the ballast resistor, which then causes the resistance to increase as well.
You can find this type of ballast resistor in incandescent lamps. As the current through the lamp goes up, the resistance of the ballast resistor also increases, leading to a higher voltage drop across the resistor.
When the current decreases, the temperature drops, and so does the resistance. This kind of resistor is also used to protect circuit equipment from too much current.
Adjustable Ballast Resistors
Also referred to as variable ballast resistors, adjustable ballast resistors enable users to modify the resistance value. This is done by altering the position of a movable contact on a resistive material. Adjustable ballast resistors are widely used in situations where precise adjustment of the resistance value is necessary for peak performance. For instance, in audio circuits, adjustable ballast resistors can be utilized to tweak the gain of an amplifier.
Apart from fixed and adjustable ballast resistors, there are other varieties such as wire-wound, metal film, and carbon film resistors. Each type of resistor has its own distinct features and is appropriate for particular applications.
In general, the type of ballast resistor chosen for a circuit depends on the specific demands of the application. Selecting the right type of ballast resistor is crucial to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Function and Importance
A ballast resistor is a device that controls the amount of current in a circuit. It is a type of resistor designed to offer a stable level of resistance, regardless of variations in current or voltage levels. The ballast resistor is a vital component in many electrical circuits and performs several key functions.
Current Regulation
One primary function of a ballast resistor is to control the current in a circuit. As the current in the circuit rises, the resistance of the ballast resistor also goes up. This helps to restrict the current flow, preventing overloading and reducing the risk of damage to other components.
Voltage Stabilization
Another crucial function of a ballast resistor is to stabilize the voltage in a circuit. The ballast resistor helps to keep the voltage level steady, even when there are fluctuations in the power supply. This is important because many electronic devices are sensitive to voltage changes, and sudden surges or drops in voltage can harm these devices.
Overall, the ballast resistor is a significant component in many electrical circuits. It helps to regulate the current and stabilize the voltage, ensuring safe and efficient circuit operation. By maintaining a consistent resistance level, the ballast resistor protects other components in the circuit from damage and ensures that the circuit functions within its intended parameters.
How to Test a Ballast Resistor
A ballast resistor is used in cars to lower the voltage going to the ignition coil. To test it, you will need an ohmmeter and a multimeter.
When the ballast resistor is not connected to the ignition coil, the full supply voltage goes to the coil. Typically, the battery for the ignition system will be either 12 volts or 24 volts.
To help the ignition coil last longer, we need to reduce the voltage, which is why we connect a ballast resistor to it.
To test the ballast resistor, you can measure the voltage across the ignition coil. If the ballast resistor is working properly, it should lower the voltage to about 7 to 8 volts. If the voltage is too high, the ballast may be damaged.
You can also check the resistance of the ballast resistor using an ohmmeter. If the resistance is close to its rated value, that is a good sign that the ballast resistor is in good condition.
Advantages
Here are some of the benefits of using a ballast resistor:
- These resistors help control the voltage and current in electrical systems.
- They protect equipment from too much voltage and too much current.
- Ballast resistors reduce fluctuations in current and voltage throughout the rest of the circuit.
- Because of these advantages, ballast resistors are mainly used for protection against over-voltage and overcurrent in various automotive and lighting circuits, helping to keep everything stable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I determine if a ballast resistor is going bad?
A weak or absent spark is often a telltale sign of a ballast resistor on the verge of failure. Moreover, the engine might struggle to start or stall often. Should you observe any of these signs, it's crucial to get your ignition system inspected by a professional.
What's the main role of a ballast resistor in an ignition system?
The main role of a ballast resistor in an ignition system is to control the voltage supplied to the ignition coil. During startup, the resistor permits a higher voltage to reach the coil for a robust spark. After the engine starts, the voltage is lowered to safeguard the coil from overheating and extend its lifespan.
What problems can arise from not using a ballast resistor?
Not using a ballast resistor can lead to the ignition coil overheating and failing early. This can cause poor engine performance, misfires, and other issues that are expensive to fix.
How do you wire a ballast resistor to a 12V ignition coil?
When wiring a ballast resistor to a 12V ignition coil, it's essential to closely follow the manufacturer's guidelines. In most instances, the ballast resistor should be connected in series with the positive terminal of the ignition coil. This helps regulate the voltage to the coil and prevents it from overheating.
What are the typical signs of ballast resistor problems?
Typical signs of ballast resistor problems are weak or no spark, trouble starting the engine, frequent stalling, and poor engine performance. If you notice any of these signs, it's important to have your ignition system checked by a professional.
How do you replace a faulty ballast resistor?
If you suspect your ballast resistor is faulty, it's important to replace it promptly. To replace a faulty ballast resistor, you need to disconnect the wires from the old resistor and remove it from the ignition system. Then you can install a new resistor and reconnect the wires as per the manufacturer's instructions. Using the correct type of resistor for your ignition system is vital to ensure proper function.
Related Articles
Different Types of Audio Cables and How to Pick the Right One
CBB61 Capacitors: What They Are and How to Use Them
Supercapacitor: Definition and Applications (Guide)
Thyristor Controlled Reactor (TCR) and Thyristor Switched Capacitor (TSC)
Ceramic Capacitor: Working, Construction and Applications
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













