

Intake Air Temperature Sensor: Specifications,Differences & Applications
Catalog
What is an Intake Air Temperature Sensor?How Does the Intake Air Temperature Sensor Work?Specifications of the Intake Air Temperature SensorIntake Air Temperature Sensor CircuitIAT Sensor vs MAF SensorAdvantages and DisadvantagesApplications of Intake Air Temperature SensorsWhat is a Temperature Sensor?ConclusionIntake Air Temperature Sensor FAQThe intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is crucial for improving engine performance and aiding the development of the electronic fuel injection (EFI) system. It has been in use since the early EFI systems, helping to measure air density for accurate air-fuel ratio adjustments. The market for IAT sensors is growing globally, with forecasts indicating continued growth in the coming years. Today, these sensors are a standard feature in most modern vehicles and are vital components within engine management systems. This article explains the role of the intake air temperature sensor, how it works, and its various applications.
What is an Intake Air Temperature Sensor?
An intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a two-wire thermistor designed to measure the temperature of the air entering the engine. It sends this critical data to the Engine Control Unit (ECU), which uses it to optimize fuel delivery and engine performance. This data is vital because air density changes with temperature, affecting combustion efficiency.
The ECU relies on the IAT sensor to determine the precise amount of fuel needed for optimal combustion. The sensor’s main role is to provide the ECU with accurate temperature readings, allowing it to adjust the air-fuel mixture and ignition timing accordingly.
The IAT sensor’s resistance varies with temperature, and the ECU detects these changes to calculate the air temperature. These sensors are typically located in areas like the intake air tube, between the air filter box and throttle body, or even integrated into the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor.
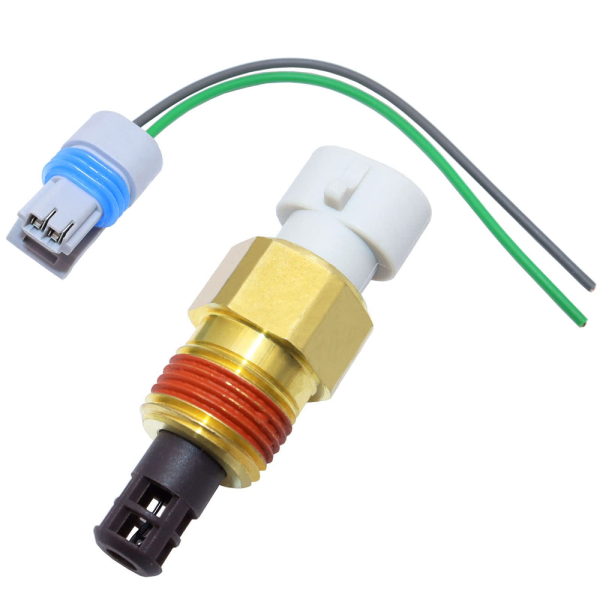

intake air temperature (IAT) sensor
How Does the Intake Air Temperature Sensor Work?
The intake air temperature sensor works by measuring the temperature of the air entering the engine and sending this data to the ECU, which uses it to optimize fuel delivery and engine performance. The sensor uses a thermistor, which is a type of resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. As the temperature changes, so does the resistance, and this alters the voltage signal sent to the ECU.
The ECU provides a reference voltage to the thermistor, and as its resistance changes with temperature, the voltage signal varies. This signal is then sent back to the ECU, which interprets it to determine the intake air temperature. The ECU uses this information to adjust the air-fuel mixture and other engine parameters for optimal performance and fuel efficiency.
Specifications of the Intake Air Temperature Sensor
The key specifications of the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor include:
- The IAT sensor is a two-wire thermistor.
- Temperature accuracy typically ranges from ±2°C to ±5°C.
- It has a fast response time.
- The sensor's resistance changes with temperature, generally decreasing as the temperature increases.
- The resistance at 25°C usually falls between 2.0 kΩ and 5.0 kΩ.
- The sensor is typically mounted in the air filter box or intake manifold.
- It uses a standard connector like the Bosch EV1 connector.
- The connector type is AMP SCS (Sealed Connector System).
- The operating temperature range is from -40°C to 125°C.
- The storage temperature range is from -40°C to 130°C or higher.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit
The intake air temperature sensor is connected to the Engine Control Module (ECM) circuit as shown below. The ECM provides a 5V supply voltage to the IAT sensor, which enters the thermistor through the THA terminal and exits through the E2 terminal on the ECM.
When the air entering the intake manifold is cold, the resistance of the sensor is high. As a result, the voltage signal from the IAT sensor is lower. Conversely, when the air temperature increases, the sensor's resistance decreases, leading to an increased voltage signal being transmitted to the ECM. This voltage is then used by the ECM to adjust the engine's air-fuel mixture for optimal performance.
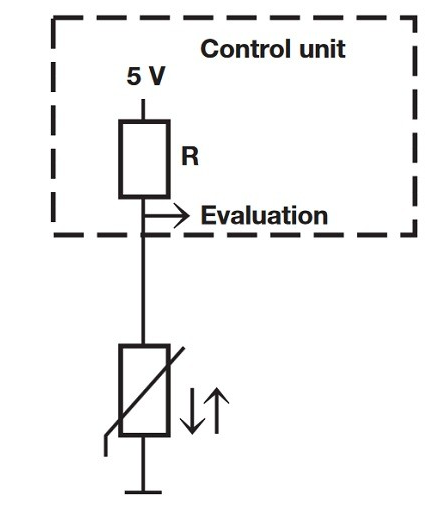
Intake Air Temperature Sensor Circuit
Whenever the air temperature entering the intake manifold increases, the resistance of the sensor decreases, causing the voltage sent to the ECM to rise.
The voltage change in the IAT sensor is directly linked to the temperature variation detected by the ECM. This data is crucial for determining the appropriate amount of fuel to inject into the engine’s cylinders. If the sensor detects a higher air temperature, the ECM may increase the fuel injection by extending the injector's opening time. On the other hand, if the air temperature is lower, the ECM may reduce the fuel injection by shortening the injector’s opening time.
Therefore, the intake air temperature sensor (ATS) is a key component of modern fuel injection and ignition systems. By measuring the temperature of the air entering the engine, it provides the ECM with valuable information, enabling necessary adjustments to ensure optimal engine performance.
IAT Sensor vs MAF Sensor
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor and the mass air flow (MAF) sensor both play important roles in optimizing engine performance, but they measure different parameters and function in different ways. Below is a comparison of the two sensors:
| IAT Sensor | MAF Sensor |
|---|---|
| Measures only the air temperature entering the engine. | Measures both the mass of the air and the air temperature entering the engine. |
| Provides the ECU with data on air temperature, helping to optimize fuel delivery and ignition timing. | Provides the ECU with comprehensive data on air intake, allowing for precise fuel control. |
| Uses a two-wire thermistor that changes resistance in response to temperature changes. | Uses a heated wire or film that is exposed to incoming air to measure mass flow. |
| Simple in design and function. | More complex than the IAT sensor. |
| Typically located in the intake air tube, integrated into the MAF sensor, or within the inlet manifold. | Usually located between the air filter and the intake manifold. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of IAT Sensors
- Engine Optimization: Helps the ECU optimize engine performance and fuel delivery by accurately measuring the air entering the engine, which affects air density and the amount of fuel needed for combustion.
- Improved Fuel Economy and Emissions: By providing accurate data on air temperature, it allows for better control of the air-fuel mixture, resulting in superior fuel economy, reduced emissions, and improved engine performance.
- Prevents Engine Damage: It can detect potential issues such as excessive intake air temperature, preventing engine damage from conditions like detonation.
- Vital in Motorsports: Essential for ensuring reliable engine performance in high-performance environments like motorsports.
- Emission Control: Plays a key role in controlling emissions by helping the engine run with the optimal air-fuel mixture.
- Diagnostic Tool: Provides critical data for engine management, thermal protection, and diagnostics by keeping the engine within safe operating parameters.
- Reliable and Durable: Known for being a durable and reliable component in modern engines.
- Easy Installation: Can be easily integrated into engine monitoring systems.
Disadvantages of IAT Sensors
- Faulty Sensor Issues: A malfunctioning IAT sensor can cause issues like incorrect air-fuel ratio calculations, leading to poor engine performance, higher fuel consumption, and inefficient combustion.
- Engine Problems: A faulty sensor may send incorrect temperature readings to the ECU, resulting in poor engine performance, stalling, hesitation, rough idling, decreased power, or difficulty starting the engine.
- Reduced Efficiency: If the air-fuel mixture is incorrect due to faulty sensor data, the engine will run inefficiently, increasing fuel consumption.
- Risk of Long-Term Damage: Ignoring a faulty IAT sensor can lead to significant engine damage over time due to continuous operation with incorrect air-fuel mixture.
- Malfunction Indicator: A faulty sensor will trigger the Malfunction Indicator Light (MIL) on the dashboard and store a fault code in the ECU.
- External Damage Issues: Sensors can be affected by external factors like rust, dirt, poor connections, or damaged wiring.
- Impact on EGR: In some cases, the IAT sensor is used to control the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve. A faulty sensor can affect the EGR system’s operation and increase emissions.
- Limp Mode Activation: A faulty IAT sensor can cause the engine to enter limp home mode, limiting performance until the sensor issue is addressed.
Applications of Intake Air Temperature Sensors
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in optimizing engine performance and fuel efficiency. Here are some of the primary applications:
- Engine Performance Optimization: The IAT sensor measures the air temperature entering the engine, providing essential data to the ECU for optimizing fuel delivery and engine operation.
- Air-Fuel Ratio Control: The ECU uses the IAT data to adjust the air-to-fuel ratio, ensuring efficient combustion and peak engine performance.
- Air Mass Calculation: The IAT sensor works alongside other sensors to help the ECU calculate the air mass entering the engine, further improving performance.
- Ignition Timing Adjustment: The IAT data allows the ECU to fine-tune the ignition timing, optimizing engine performance under various conditions.
- Standard in Modern EFI Systems: IAT sensors are integral to modern Electronic Fuel Injection (EFI) systems, providing critical information for engine control and fuel efficiency.
- Diesel and Petrol Engines: These sensors are used in both diesel and petrol engines to optimize fuel delivery and enhance engine performance.
- Motorsport Applications: In motorsports, IAT sensors help optimize engine performance, ensuring reliable fuel delivery and performance under changing conditions.
- Household and Industrial Use: IAT sensors are also used to measure air intake temperature in household and industrial applications.
- HVAC Applications: Some IAT sensors can be used in HVAC systems to monitor air duct temperatures, especially in non-condensing applications.
What is a Temperature Sensor?
A temperature sensor is a device used to measure temperature and convert this measurement into an electrical signal that can be read and interpreted by a monitoring system or control unit. Temperature sensors are used in a wide variety of applications, from monitoring engine performance (like the IAT sensor) to household heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. They come in various types, including thermocouples, thermistors, and resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), each suitable for different temperature ranges and levels of accuracy.
Conclusion
The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a vital component in modern engine management systems. It measures the temperature of the air entering the engine and provides this data to the ECU, which uses it to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, and overall engine performance. By ensuring the correct air-fuel mixture and adjusting engine parameters, the IAT sensor enhances fuel efficiency, reduces emissions, and prevents engine damage. These sensors are used in both petrol and diesel engines, in motorsports, and even in industrial and HVAC applications. Despite their advantages, faulty IAT sensors can lead to performance issues, increased fuel consumption, and engine damage, making them an essential part of vehicle diagnostics and maintenance.
Intake Air Temperature Sensor FAQ
What is an Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor?
The IAT sensor measures the temperature of the air entering the engine. This data is sent to the ECU (Engine Control Unit) to optimize fuel delivery, ignition timing, and overall engine performance.
Why is the IAT sensor important?
The IAT sensor is crucial for maintaining optimal air-fuel mixture and ignition timing. By measuring air temperature, it helps the ECU adjust engine parameters for efficient combustion, better fuel economy, and reduced emissions.
How does the IAT sensor work?
The IAT sensor uses a thermistor whose resistance changes with temperature. The ECU supplies a reference voltage to the sensor, and as the temperature of the incoming air changes, the resistance of the sensor varies, producing a corresponding voltage signal that the ECU interprets to adjust engine performance.
Where is the IAT sensor located?
The IAT sensor is typically located in the intake air tube, between the air filter and the throttle body, or it may be integrated into the Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor or the intake manifold.
What are the symptoms of a faulty IAT sensor?
A malfunctioning IAT sensor can cause issues like poor engine performance, reduced fuel economy, rough idling, hesitation, stalling, difficulty starting the engine, and increased emissions. A faulty sensor will also trigger the Check Engine Light (CEL) and store a fault code in the ECU.
Can a faulty IAT sensor affect fuel economy?
Yes, a faulty IAT sensor can lead to incorrect air-fuel mixture calculations, resulting in inefficient combustion and higher fuel consumption.
How do I know if my IAT sensor is bad?
Common signs of a faulty IAT sensor include poor engine performance, difficulty starting the engine, rough idling, stalling, and poor acceleration. Additionally, the Check Engine Light (CEL) may illuminate, and diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) related to the IAT sensor will appear when scanned.
Can I drive with a bad IAT sensor?
While the engine may still run with a faulty IAT sensor, driving with a malfunctioning sensor is not recommended. It can lead to poor engine performance, decreased fuel efficiency, and long-term engine damage if not addressed.
How do I replace an IAT sensor?
Replacing an IAT sensor typically involves locating the sensor (usually in the intake air tube or near the MAF sensor), disconnecting the electrical connector, removing the old sensor, and installing a new one. It’s a relatively simple procedure, but it's advisable to consult your vehicle’s manual or seek professional help if you're unsure.
How often should the IAT sensor be replaced?
The IAT sensor typically does not require frequent replacement. However, it should be inspected if you experience performance issues, and it may need replacement if it's found to be faulty during diagnostics.
Can the IAT sensor be cleaned?
In some cases, cleaning the IAT sensor may improve performance if dirt or debris has built up on it. However, if the sensor is damaged or malfunctioning, it will need to be replaced. Always consult your vehicle’s manual for proper maintenance procedures.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













