
What Is Software-Defined Networking ?
Catalog
What Is SDN?The Four Main Types of Software-Defined Networking The Advantages of Software-Defined Networking Why Software-Defined Networking Is Important?Frequently Asked Questions: Related ArticlesWhat Is SDN?
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is an innovative networking paradigm that separates the network control layer from the data forwarding layer, allowing network administrators to manage network services through centralized software applications. Here's a concise explanation of SDN and its workings:
1. Centralized Control: SDN centralizes network control on a software platform, which is typically a controller that uses APIs to manage network behavior and make decisions about where network traffic is sent.
2. Separation of Control and Data Planes in SDN: The SDN architecture separates the network's control and data forwarding functions, which enables the control aspect to be programmable and the network infrastructure to be virtualized for the benefit of applications and services.
3. Adaptability and Expandability: By separating the control plane from the data plane in SDN, there is an enhanced capacity for adaptability and expandability in managing networks. This enables network administrators to modify network settings with increased speed and efficiency.
4. Programmability: SDN enables network programmability, which means that network behavior can be modified and customized through software, without the need for manual changes to hardware configurations.
5. Network Virtualization Enhancement: SDN facilitates the establishment of numerous virtual networks atop a single physical infrastructure, which optimizes the use of resources and promotes the swift deployment of services.
6. Traffic Management: SDN simplifies traffic management by allowing for the centralized control of data packet routing. This can lead to more efficient and intelligent traffic management, as the controller can make routing decisions based on a global view of the network.
7. Interoperability: SDN can improve interoperability by allowing different network devices from various vendors to work together under a unified control system.
8. Automation: SDN supports network automation, which can reduce the time and effort required to manage complex networks, as well as decrease the likelihood of human error.
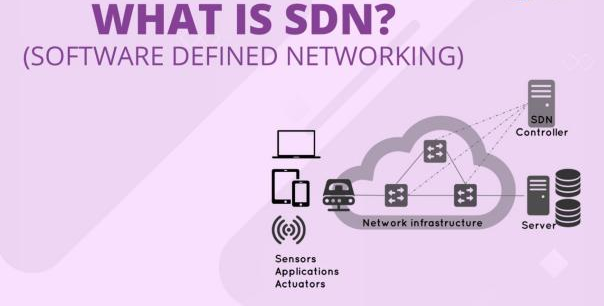

What is SDN?
The Four Main Types of Software-Defined Networking
1. Open SDN: This type of SDN leverages open standards and protocols for controlling both virtual and physical network devices that handle data packet routing. The openness allows for collaboration among different groups, including network operators, developers, and vendors, which can lead to better optimization of network operations.
2. API SDN: In this model, southbound APIs are used to manage the flow of data to and from network devices. API SDN facilitates the integration of orchestration platforms, cloud management tools, and network management systems with the SDN infrastructure, enabling more automated and streamlined network operations.
3. Overlay Model SDN: With the overlay model, virtual networks are superimposed on existing hardware infrastructure. It creates tunnels that span both remote and local data centers, managing bandwidth allocation and device assignment to these tunnels.
4. Hybrid Model SDN: This approach combines elements of SDN with traditional networking to determine the best protocol for different types of network traffic. The hybrid model is often used as a transitional strategy, allowing organizations to gradually adopt SDN within their existing network environments.

Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
The Advantages of Software-Defined Networking
1. Ease of Network Control: By decoupling the control plane from the data plane, SDN allows for centralized management of network devices. This simplifies the process of configuring and managing network services in real-time, leading to more efficient network operations.
2. Agility: SDN's ability to dynamically adjust to traffic fluctuations through load balancing reduces latency and improves network performance. This agility is crucial for organizations that require rapid responses to changing network demands.
3. Flexibility: The software-based control layer in SDN provides network operators with the flexibility to quickly adapt to changes in network requirements. This includes the ability to modify configurations, provision resources, and scale network capacity as needed.
4. Greater Control over Network Security: SDN centralizes security policy enforcement, allowing administrators to define and enforce access control and security policies across the entire network from a single point. Micro-segmentation further enhances security by simplifying the management of network segments.
5. Simplified Network Design and Operation: With SDN, administrators can use a single protocol to communicate with a variety of hardware devices through a central controller. This standardization simplifies network design and operation, and reduces reliance on proprietary devices and protocols.
6. Modernizing Telecommunications: The combination of SDN with virtualization technologies enables service providers to offer more flexible and scalable services. Customers can benefit from network separation and control tailored to their specific needs, with the ability to adjust bandwidth on demand, which is particularly valuable for businesses with variable network usage.

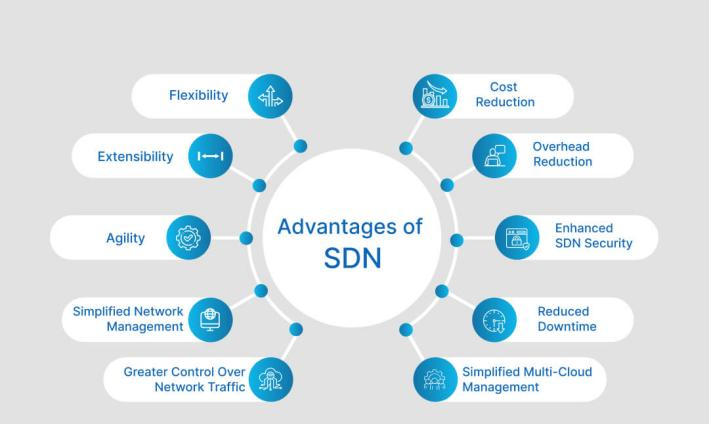

The advantages of Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Why Software-Defined Networking Is Important?
1. Increased Control with Greater Speed and Flexibility: SDN allows for a more agile and responsive network infrastructure. By centralizing control in software, network administrators can make changes quickly and easily, without having to touch each device individually. This speed and flexibility are particularly valuable in dynamic environments where network requirements can change rapidly.
2.Customizable Network Infrastructure: SDN enables network administrators to programmatically configure and reconfigure network services and resources in real-time. This level of customization allows for the optimization of network traffic and the prioritization of critical applications, leading to improved performance and service delivery.
3. Robust Security: SDN provides a single pane of glass for network visibility, making it easier to monitor and manage security across the entire network. With the ability to segment the network and apply granular security policies, SDN can help contain threats and protect against breaches more effectively than traditional networks.
4. Infrastructure Differences: The shift from hardware-based to software-based control is a fundamental change in networking. SDN's software-based control plane allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as it can be updated and adapted more quickly than hardware-based systems. This means networks can evolve with changing business needs without the constraints of physical infrastructure.
5. Security Differences: SDN's centralized control plane offers improved security through better visibility and the ability to enforce consistent security policies across the network. However, as you pointed out, the central controller becomes a critical point that must be secured to maintain network security. This requires robust security measures to protect the controller from attacks.
6. Cost Savings and Efficiency: SDN can reduce costs by allowing the use of commodity hardware and by automating many network functions that would otherwise require manual configuration. This efficiency can lead to significant savings for organizations.
7. Innovation and Speed to Market: With SDN, new network services can be developed and deployed more quickly. This accelerates the time to market for new applications and services, giving organizations a competitive edge.
8. Scalability and Elasticity: SDN's ability to dynamically allocate resources means that networks can scale up or down to meet demand, providing elasticity that is particularly useful for cloud services and large-scale data centers.


Why Software-Defined Networking is important?
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What is a Software-Defined Network?
SDN is a networking paradigm where network control is decoupled from the hardware and provided by a centralized software application called a controller. This controller uses APIs to manage the network devices, making the network more flexible and responsive to changes in the infrastructure.
2. What SDN Means?
SDN means that the network's behavior and policies are determined by software, rather than by the hardware itself. This allows for a more programmable and agile network that can be adjusted and optimized in real-time to meet changing demands.
3. What is an Example of Network Software?
Examples of network software include:
Network Management Tools: Such as SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) managers.
Firewalls: Software that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules.
Network Operating Systems: Like Cumulus Linux or NOS (Network Operating System) that manage the operation of network devices.
Protocol Support Applications:Software that supports various network protocols such as BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) or OSPF (Open Shortest Path First).
4. Why Use SDN?
Organizations use SDN for several reasons:
Improved Network Performance:By optimizing traffic flow and load balancing, SDN can reduce latency and increase efficiency.
Cost Savings: SDN can reduce the need for specialized hardware, leading to cost savings.
Scalability:SDN can handle large-scale networks more effectively, making it ideal for cloud environments.
Innovation: SDN enables faster development and deployment of new network services.
5. What are the Two Main Challenges of SDN?
Controller Complexity:The centralized controller can become a single point of failure and a bottleneck, requiring careful design and redundancy.
Scalability: As networks grow, the controller must efficiently manage a large number of devices without performance degradation.
6. What is the Purpose of Software-Defined Networking?
The purpose of SDN is to simplify network management and operations by abstracting the control plane from the data plane. This allows for more dynamic, flexible, and programmable networks that can be adjusted on the fly to meet changing business needs.
Related Articles
This article is from JMBom Electronics,which cooperates with manufacturers and offer electronic components, semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes,transistors, lCs.and resistors. For more product information, please go to the website to get it.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













