

What is a Solenoid Switch
Catalog
What is a Solenoid Switch?Different types of solenoids switchesSolenoid Switch FeaturesWhat are the different kinds of electromagnetic solenoids?How to Connect a Solenoid SwitchHow Does a Solenoid Switch Work?Applications of Solenoid Switches Advantages of Solenoid SwitchesConclusionRelated ArticlesElectromagnetic switches are a common control device used to open and close electrical circuits.
What is a Solenoid Switch?
A solenoid switch is a widely used control device designed to interrupt or activate current circuits. It operates on the principle of electromagnetism, utilizing an electromagnetic coil to toggle devices on and off. These switches are frequently found in various electrical equipment, automation systems, and power distribution networks, playing a crucial role in circuit control. The solenoid switch comprises an electromagnetic coil, contacts, and a drive mechanism. When the electromagnetic coil is energized, it generates a magnetic field that attracts or separates the contacts, thereby opening or closing the circuit.
Exploring the detailed structure of a solenoid switch reveals that several key components work together to enable its electromechanical function. At the heart of the solenoid is a coil, typically made from copper wire, which wraps around the core. When an electric current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field. The core, made from ferromagnetic material, plays a vital role in enhancing and concentrating this magnetic field. By providing a magnetic flux path, the core significantly boosts the solenoid's performance. The plunger, or armature, is a movable part usually made from ferrous material, positioned within the solenoid. When the solenoid is energized, the plunger is drawn toward the core. A spring mechanism ensures that the plunger returns to its original position when the electric current is cut off. This spring helps reset the solenoid switch to its default state when inactive. The coordinated interaction of these components enables solenoid switches to operate reliably and effectively in a wide range of applications.
Different types of solenoids switches
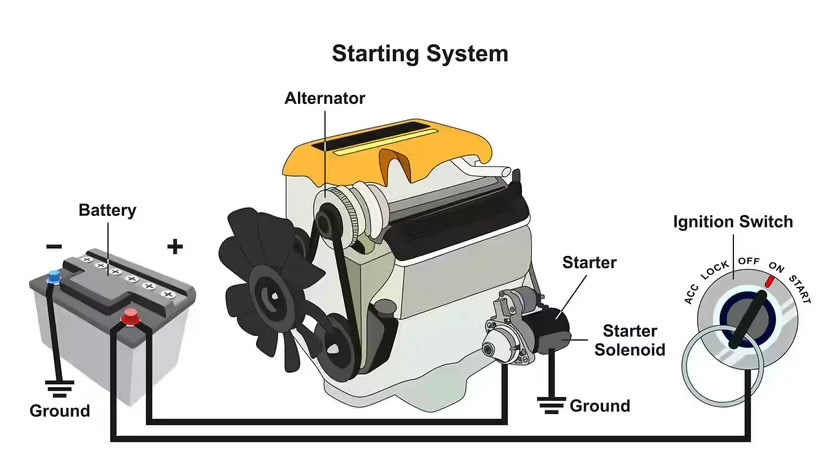
Solenoid switches are available in a wide range of types, each tailored to specific applications and functions. For instance, the starter solenoid, a special type of solenoid switch used in automobiles, is a key component in the automotive starting system. Its role is to activate and control the electromagnetic coil to open or close the circuit when the car engine is started. Below is a comprehensive overview of the different types of solenoid switches:
Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valve
Also known as an indirect-acting valve, this type uses differential pressure to regulate flow. It employs a pilot valve to control the flow of a pressurized medium, which then operates the main valve. While more complex, it offers precise control over fluid flow, making it suitable for applications requiring fine-tuned regulation. It is commonly used in hydraulic and pneumatic systems where precise fluid flow control is essential.
Two-Way Solenoid Valves
Designed for simplicity and reliability, these valves have two ports that either allow or restrict fluid flow. They can be configured as normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC), depending on the specific application requirements.
AC Laminated Solenoid
These switches are designed for alternating current (AC) applications and feature laminated cores to minimize eddy current losses. They are used in applications that require high inrush current and where the solenoid must handle AC power.
Linear Solenoid
This type provides linear motion, converting magnetic force into straight-line action. Linear solenoids are used in applications that require precise positioning or actuation, such as in robotics and automated machinery.
Three-Way Solenoid Valve
With three ports and two distinct orifices, these valves are adept at mixing or diverting fluid streams. Their alternating opening mechanism makes them essential in applications involving the combination or separation of fluids.
Four-Way Solenoid Valve
These valves represent the pinnacle of control, with four ports that manage both pressure inlets and exhaust outlets. They are often found in complex systems where precise fluid flow manipulation is critical.
Direct Acting Solenoid Valve
These are the industry workhorses, providing a straightforward and efficient way to control fluid flow. They operate by directly translating the linear motion of the solenoid into the movement of a valve plug or disc, offering a rapid and reliable response.
Solenoid Switch Features
Electromagnetic Functionality
Solenoid switches are electrically powered and operate via electromagnetic principles.
Highly Reliable
With minimal moving components, solenoid switches offer high durability and dependability.
Broad Voltage Compatibility
These switches can function across a wide voltage spectrum, from low-voltage DC systems to high-voltage AC applications.
Energy Efficient
Consuming very little power, solenoid switches are both energy-efficient and cost-effective.
Weatherproof
Many solenoid switches are built to withstand outdoor conditions, ensuring reliable operation in various environments.
Customizable Features
Solenoid switches can be tailored to specific needs, including mounting styles, contact arrangements, and voltage ranges.
Quick Switching
Solenoid switches can generally switch circuits in just a few milliseconds. They are known for their quick response, which makes them ideal for applications that require efficient switching.
Extended Lifespan
Solenoid switches can withstand millions of on/off operations, giving them a long lifespan. Traditional mechanical switches, however, do not have nearly as long a lifespan as solenoid switches.
High Dependability
Solenoid switches are highly dependable, with the ability to operate stably and work for extended periods without failure. They are designed to be simple yet effective, and they can handle high currents and voltages. Moreover, the contacts are specially treated to resist arcing and wear, which helps extend the switch's service life. This high reliability makes solenoid switches a crucial component in a variety of industrial and commercial equipment.
Compact and Portable
Solenoid switches are usually smaller and lighter than other types of switches. This makes them easy to install and transport. Their compact size and portability are advantageous in environments where space is limited, and they are also easy to repair and replace.
What are the different kinds of electromagnetic solenoids?
Electromagnetic solenoids are devices that utilize the magnetic field created by an electric current flowing through a coil to perform various functions. While solenoid switches specifically focus on controlling electrical circuits through electromagnetic force, the broader category of electromagnetic solenoids encompasses a wider range of devices that apply electromagnetic principles. Familiarizing ourselves with the diverse types of electromagnetic solenoids can provide valuable insights into the variety and applications of electromagnetic equipment. Here are some common types of electromagnetic solenoids:
Electromagnetic solenoid: This refers to devices that harness the magnetic field generated by a current-carrying coil to achieve mechanical movement, switching actions, or other control functions. These devices are integral to numerous applications, including industrial control, automotive engineering, mechanical transmission systems, and more. There are various types of electromagnetic solenoid switches, all of which employ electromagnetic principles to control or operate different mechanical or electrical equipment. Examples include electromagnetic clutches, electromagnetic brakes, solenoid valves, and ignition switches.
Electromagnetic clutch switch: This type of switch controls the engagement of a clutch based on electromagnetic principles. In mechanical transmission systems, activating the electromagnetic clutch switch causes the clutch to engage, enabling power transmission. This switch is extensively used in vehicles and mechanical equipment.
Electromagnetic brake switch: This switch is designed to control the activation and deactivation of brakes. When the switch is activated, the brake generates a stopping force to halt the movement of equipment or vehicles. This type of switch is commonly used in vehicles, elevators, and mechanical equipment where precise braking control is necessary.
Solenoid valve: Solenoid valves are crucial components for controlling the flow of liquids and gases through a network of pipes and channels. These valves are not just mechanical devices; they represent precision and reliability, ensuring accurate fluid flow regulation. A solenoid valve operates on the principle of electromagnetism, using a plunger or diaphragm mechanism to control fluid flow. Imagine the coil as an electromagnet and the contacts as pieces of iron. When energized, the magnetic field attracts the iron filings, causing them to fit together. When power is cut off, the magnetic field disappears, and the iron piece opens due to its spring force. This principle offers reliability and rapid response, making solenoid valves ideal for applications requiring precise fluid control.
Ignition switch: In devices with internal combustion engines, the ignition switch controls the ignition process. For instance, in a car engine, the ignition switch controls the operation of the ignition coil, which ignites the air-fuel mixture.
How to Connect a Solenoid Switch
Connecting a solenoid switch entails linking the solenoid to a power supply and a control signal to trigger it. The precise wiring configuration may differ based on the particular solenoid switch and its designated use. Below is a general guide for connecting a solenoid switch:
Materials Required:
- Solenoid switch
- Power source (battery or power supply unit)
- Control switch or relay
- Electrical wires
- Wire connectors
- Wire strippers
- Electrical tape
- Steps for Connecting a Solenoid Switch:
Locate Solenoid Terminals:
- The majority of solenoids feature at least two terminals: one for power (commonly marked with a "+" symbol) and one for ground or return.
Set Up Power Source:
- Attach the positive terminal of the power source (battery or power supply unit) to the power terminal of the solenoid.
- Link the negative terminal of the power source to the ground terminal of the solenoid.
Control Signal Wiring:
- If employing a control switch or relay to activate the solenoid, connect one end of the control signal wire to the control terminal on the solenoid.
- Connect the other end of the control signal wire to the control switch or relay.
Control Switch or Relay:
- If using a control switch, connect one terminal of the switch to a power source and the other terminal to the control terminal of the solenoid.
- If using a relay, connect the control signal wire to the appropriate terminal on the relay.
Secure Connections:
- Utilize wire connectors to fasten the connections between wires and terminals.
- Ensure all connections are snug and adequately insulated.
Testing:
- Before finalizing the wiring, meticulously check all connections.
- Test the solenoid switch by applying power and activating the control signal to verify proper operation.
Insulation:
- Once testing is successful, use electrical tape to insulate exposed wires and connections to avert short circuits.
Safety Precautions:
- Always disconnect the power source prior to wiring to avert electrical shock.
- Double-check all connections to ensure they are secure and accurate.
- Adhere to any specific wiring instructions provided by the solenoid manufacturer.
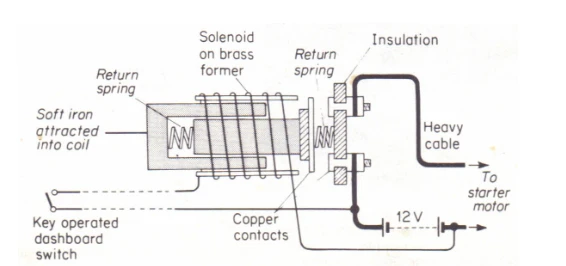
How Does a Solenoid Switch Work?
A solenoid switch functions by utilizing electromagnetic principles. It includes a wire coil, usually wrapped around a movable core called an armature. The core mechanism relies on creating an electromagnetic field when an electric current passes through the coil.
Electric Current Flow: When an electric current passes through the coil, it generates a magnetic field around it due to the movement of electrons in the wire.
Electromagnetic Field Creation: This magnetic field induces magnetism in the armature, the movable core inside the solenoid.
Armature Motion: Depending on the current’s direction, the armature is either drawn toward or pushed away from the coil by the electromagnetic force, causing it to move.
Mechanical Action: The movement of the armature is used to carry out mechanical tasks. In a solenoid switch, this often involves opening or closing valves, switches, or other components.
Energy Conversion: The solenoid converts electrical energy into mechanical movement and force, which is crucial in applications requiring controlled switching or motion.
In a solenoid switch, the armature's movement is intended to open or close the switch contacts, which controls the flow of electrical current by either allowing or stopping it. This precise switching mechanism is widely used in various devices and systems, such as automotive starters and industrial control equipment.
In conclusion, a solenoid switch utilizes electromagnetic forces generated by an electric current passing through a coil to move the armature, enabling mechanical actions like switching circuits on or off. This electromechanical function makes solenoid switches highly adaptable components in many industries and applications.
Applications of Solenoid Switches
Motor Control
One of the most prevalent uses for solenoid switches is in motor control systems. These systems typically employ solenoid switches to activate or deactivate circuits, thereby controlling the motor's direction (forward and reverse), as well as its starting and stopping. Solenoid switches are known for their rapid switching capabilities, as well as their resistance to dust, water, and explosions. These characteristics not only ensure efficient operation but also protect the motor and extend its lifespan.
Lighting Control
Solenoid switches are extensively utilized in indoor lighting control systems. In contemporary homes, they have become a standard feature for managing lighting. By connecting the light source to the solenoid switch, users can control the circuit to achieve functions such as turning the lights on and off, and dimming. This not only conserves energy but also enhances home automation and improves the overall quality of life.
Air-Conditioning Control
Solenoid switches are frequently used in air-conditioning control systems in public spaces such as offices and shopping malls. By connecting the solenoid switch to the air conditioner's power supply circuit, users can control the air conditioner's start, stop, and temperature adjustment functions through the circuit switch. This helps to save energy and improve the efficiency of air-conditioning systems.
Advantages of Solenoid Switches
Solenoid switches offer rapid switching and long service life, making them ideal for applications that require high efficiency and frequent switching. They are designed to be dustproof, waterproof, and explosion-proof, allowing them to operate effectively in harsh environments. Additionally, their compact size and lightweight design make them easy to install and maintain.
Conclusion
The solenoid switch is a control device that operates based on electromagnetic principles, designed to open or close electrical circuits. It is known for its high reliability, rapid response time, and lightweight, portable design. As a crucial electrical component, the solenoid switch finds application in a broad range of fields.
If you want to know more, our website has product specifications for SolenoidcSwitches, you can go to JMBom to get more information.
Related Articles
Pushbutton Switches:Description,Applications and Types
Integrated Circuits: Features and Functions (2025)
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













