
Digital Thermometers and Their Applications
Catalog
What is a Thermometer?Two Common Types of Thermometers Used in the PastDefining a Digital ThermometerComponents of a Digital ThermometerPrinciple of Working of a Digital ThermometerA Digital Thermometer Kit Using the DS1620 Temperature SensorModern Digital ThermometersAdvantages of Digital ThermometersApplications of Digital ThermometersConclusionFrequently Ask QuestionsWhat is a Thermometer?
A thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature of an object or living being and display the reading. The temperature scale can be in Fahrenheit or Celsius.
Two Common Types of Thermometers Used in the Past
- Mercury Thermometers: These thermometers consist of a sealed glass tube with a bulb at one end filled with mercury. The basic principle behind these thermometers is that liquids expand when heated. However, they have a few drawbacks. For one, they can only measure temperatures within a certain range. Since the readings are based on the expansion of mercury, they can be inaccurate and prone to errors. Additionally, if the thermometer breaks, the mercury inside can be hazardous. For safety reasons, these thermometers need to be handled with care. Mercury also has a low freezing point, which makes these thermometers unsuitable for use in cold environments.
- Bimetallic Thermometers: These thermometers are made from two different metals joined together. As the metals heat up, they expand at different rates, causing the metal strip to bend. This bending moves a pointer on a dial with a calibrated temperature scale to show the temperature. These thermometers can also be used to control temperature. For instance, they can be connected to a switch that opens or closes as the temperature changes, making them useful for applications like ovens or refrigerators. However, these thermometers are also fragile, and their calibration is not always precise. The accuracy can shift over time, and they aren't suitable for use in very low temperatures.
After reading the information above, you should have a better understanding of thermometers and the need for a shift to a more modern approach. The key issues with the two types of thermometers discussed lie in both their basic operating principles and the display methods used. A simple solution to these problems is to replace both the underlying principle and the way the temperature is displayed.
Defining a Digital Thermometer
A digital thermometer uses a thermistor to sense the temperature and displays the reading on an electronic screen. These thermometers can be used for oral, rectal, or underarm temperature measurements. They typically measure temperatures ranging from 94°F to 105°F.
Components of a Digital Thermometer
- Battery: The thermometer is powered by a small button cell, such as the LR41 battery, which is made of metal and provides a 1.5V supply to the device.

LR41 (LR736) cell By Lead Holder
- Body: The body of the thermometer is made up of hard plastic and is 100.5mm long and its width varies from bottom to top, with the bottom being thinner.
Digital Medical Thermometer by rambergmedia
- Thermistor: The thermistor is a semiconductor made from ceramic material, used to sense temperature. It is positioned at the tip of the thermometer, secured with epoxy, and enclosed in a stainless steel cap for protection.
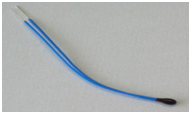
NTC bead type thermistor by Ansgar Hellwig
- LCD Display: The thermometer features an LCD display, measuring approximately 15.5mm in length and 6.5mm in width. It shows the temperature reading for 3 seconds and then begins flashing, signaling that it's ready to take the next reading.
- Circuit: The circuit includes an Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) and a microcontroller, along with several passive components, to process and display the temperature reading.
Digital Thermometer Circuit by GXTI
Principle of Working of a Digital Thermometer
A digital thermometer works by using a sensor that detects changes in resistance caused by heat. This change in resistance is then converted into a temperature reading, which is displayed digitally.
Digital Thermometer Circuit
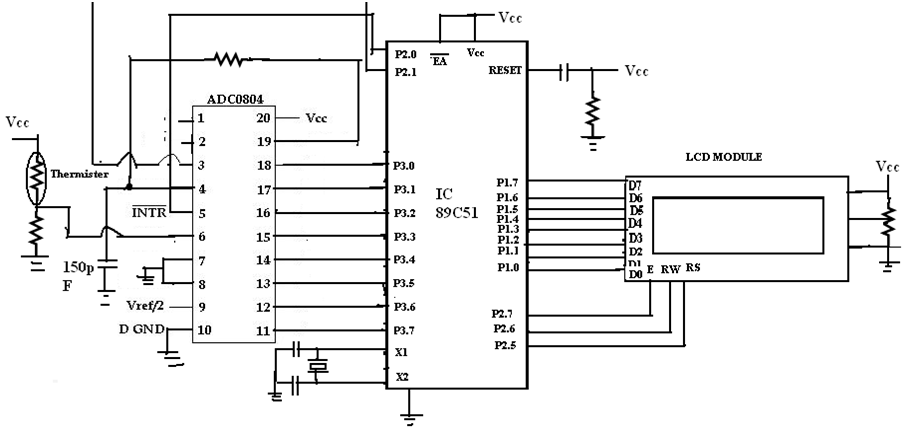
Digital Thermometer Circuit
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance changes with temperature. Depending on whether it’s a Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) or Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistor, its resistance either increases or decreases as the temperature changes. The analog signal from the thermistor is sent to the ADC, where it's converted into a digital signal. This digital signal is then passed to the microcontroller, which processes the data and displays the temperature reading on an LCD connected to it.
A Digital Thermometer Kit Using the DS1620 Temperature Sensor
In this setup, a Digital Temperature Sensor like the DS1620 is used, which provides a 9-bit digital temperature reading. This sensor is connected to the microcontroller, which receives the digital input, processes it, and then displays the temperature on the LCD connected to it.
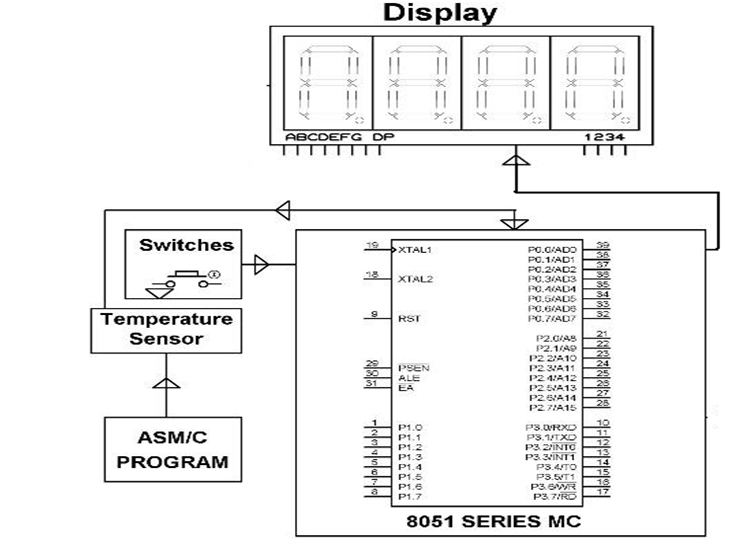
Digital Thermometer circuit diagram
The System Overview:
The system described above uses the DS1620 Temperature Sensor IC, which is an 8-pin IC capable of measuring temperatures from -55°C to +125°C. It has two pins that signal when the measured temperature exceeds a user-defined threshold, making it useful for controlling load switching in response to temperature fluctuations.
In the system, the temperature sensor first measures the ambient temperature, converts it into digital data, and sends it to the microcontroller. The microcontroller then displays the temperature on the connected display. Users can set the desired temperature threshold using a push button. If the ambient temperature moves above or below the user-defined temperature, the microcontroller controls the switching of a relay to manage the load accordingly.
Modern Digital Thermometers
- Digital Thermometer (Model: ECT-1): This thermometer measures temperatures from 32°C to 42°C with an accuracy of 0.1°C. It is primarily used in medical applications for accurate body temperature readings.
- Digital Thermometer (Model: EFT-3): This model measures temperatures from 50°C to 125°C, making it suitable for use with solid and liquid foods.
- Thermolab Digital Thermometer (IP65 Rated): This thermometer measures temperatures in the range of 50°C to 200°C with an accuracy of ±1°C. It is commonly used for industrial and laboratory applications where higher temperature ranges are needed.
Advantages of Digital Thermometers
- Accuracy: The temperature reading is directly displayed, eliminating the need to interpret a scale. This ensures precise and accurate readings every time.
- Speed: Digital thermometers provide faster readings, typically reaching a final temperature within 5 to 10 seconds, compared to the slower response times of traditional thermometers.
- Safety: Since digital thermometers don't use mercury, the risks associated with mercury poisoning are eliminated in the event of a breakage.
- Durability: There's no need to shake the thermometer to reset the mercury level, which reduces the risk of the thermometer tube breaking.
Applications of Digital Thermometers
- Medical Applications: Digital thermometers are commonly used to measure human body temperature, typically around 37°C. They are available in probe-type or ear-type designs and can measure temperature orally, rectally, or under the armpit.
- Marine Applications: In marine settings, digital thermometers with high-temperature exhaust gas sensors are used to monitor local temperatures, ensuring efficient engine and system performance.
- Industrial Applications: These thermometers are crucial in industries like power plants, nuclear power plants, blast furnaces, and shipbuilding. They can measure a wide range of temperatures, from -220°C to +850°C, making them suitable for extreme industrial conditions.
Conclusion
Digital thermometers offer a reliable, fast, and safe alternative to traditional thermometers. With their high accuracy, quick response time, and ease of use, they are widely used across various fields, from medical to industrial applications. By eliminating the risks associated with mercury and offering precise digital readings, they are an essential tool in both everyday and specialized temperature monitoring. Whether used for measuring body temperature or for industrial temperature control, digital thermometers continue to provide a practical solution in a variety of settings.
Frequently Ask Questions
What is a digital thermometer?
A digital thermometer is an electronic device that measures temperature using a sensor, such as a thermistor or thermocouple, and displays the result as numbers on a digital screen. These thermometers provide fast and accurate readings and can be used to measure temperature orally, rectally, or under the arm. They're also commonly used in industrial and food safety applications.
Can I use my smartphone as a thermometer?
No, most smartphones aren't designed to measure temperature accurately. However, some high-end models, like certain Google Pixel phones, have built-in infrared sensors that can measure the surface temperature of objects. For ambient or body temperature, you typically need an external device, although some older phones included this feature, and there are apps that estimate body temperature using the phone's internal sensors.
How do I use a digital thermometer?
To use a digital thermometer, turn it on and place the tip in your mouth, under your arm, or in your rectum. Wait for the beep, then remove the thermometer and read the temperature on the screen. For oral readings, place the tip under your tongue towards the back of your mouth, close your lips, and breathe through your nose.
Which thermometer is no longer recommended for use?
Mercury thermometers, which were once common in medicine cabinets, are no longer recommended. These thermometers use mercury encased in glass to measure temperature, but they pose a danger if broken, as mercury is toxic and can escape.
What are the disadvantages of using a digital thermometer?
Some disadvantages of digital thermometers include:
- The need for regular battery replacement.
- While cleaning a traditional thermometer with warm soapy water is straightforward, digital thermometers require more care when cleaning.
- Accuracy can vary between different models, so some digital thermometers may not be as reliable as others.
Is 99.4°F considered a fever on a digital thermometer?
Normal body temperature typically ranges from 97.5°F to 99.5°F (36.4°C to 37.4°C). It tends to be lower in the morning and higher in the evening. Most healthcare providers consider a fever to be 100.4°F (38°C) or higher. A temperature of 99.6°F to 100.3°F would be classified as a low-grade fever.
Which phone has a built-in thermometer?
The Pixel 9 Pro comes with a built-in thermometer, allowing you to check temperatures on the go – whether it's baby food or your morning coffee.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













