

Introduction to Endpoint Security
Catalog
What Is Endpoint Security?Benefits of Endpoint SecurityThe Importance of Endpoint SecurityHow Does Endpoint Security Work:What Are the Components of Endpoint Security Software?Frequently Asked Questions:Related ArticlesWhat Is Endpoint Security?
Endpoint security, is a cybersecurity strategy aimed at safeguarding endpoints, including desktops, laptops, and smartphones, against malicious actions.An Endpoint Security Platform (EPP) is a system designed to identify and fend off security risks, including file-based malware assaults and various other nefarious activities. It also offers the necessary tools for investigating and addressing the evolving nature of security breaches and warnings.


Endpoint security
Benefits of Endpoint Security
1.Endpoint security: As digital transformation pushes more employees to work remotely, protecting all endpoints has become essential to prevent breaches.
2.Identity Protection:Identity Protection is a crucial aspect of endpoint security, safeguarding the sensitive information of employees and stakeholders by ensuring that only those with proper authorization can access it.
3.Threat detection and response:With adversaries increasingly employing complex cyberattacks to infiltrate organizations, swift threat detection and response are critical for maintaining data protection and expediting the remediation process.


Benefits of Endpoint Security
The Importance of Endpoint Security
In the contemporary digital landscape, cybersecurity is a shared concern for individuals, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and multinational corporations (MNCs). The swift progress of technology has delivered many advantages, yet it has simultaneously rendered endpoints more susceptible.Employees now have the ability to access business data from their own devices and non-business networks, increasing the risk of cybercrime incidents. The COVID-19 pandemic has intensified the trend towards the deployment of weaponized AI.
1. Remote Work and Cybersecurity Risks: The move to remote work and the increased use of technology in business processes have made companies more vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Every device connected to a corporate network is a potential entry point for cyber attackers. To prevent successful attacks and reduce financial losses, it's essential to secure all endpoints that access sensitive business information, thereby protecting the company from significant financial harm.
2. Cloud and IoT Services: More businesses are adopting cloud and IoT services, which can enhance efficiency but also increase the risk of cybercrime. These services, while beneficial for streamlining processes, also expose businesses to new security challenges.
3. Consequences of Cybercrime: The impact of cybercrime is not limited to financial costs. It can also lead to missed opportunities, downtime, reputational damage, and even bankruptcy for businesses. Despite the seriousness of these risks, many businesses do not have an incident response system in place, highlighting the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect against cybercrime in a post-pandemic world.
4. Endpoint Security and Compliance: Endpoint security is vital for organizations to comply with industry-specific data protection regulations. By implementing necessary security measures and controls, endpoint security helps businesses meet their compliance obligations, which is crucial for maintaining trust and avoiding legal repercussions.


The Importance of Endpoint Security
How Does Endpoint Security Work:
1. Installation and Deployment: Organizations install endpoint security software on each device that connects to their network. This software acts as a gatekeeper, monitoring and controlling access to the device.
2. Continuous Monitoring: The endpoint security software continuously monitors the device for any suspicious activity. It scans files, processes, and systems to detect signs of malware, unauthorized access, or other threats.
3. Centralized Management: A centralized console allows administrators to manage security policies across all devices. This remote management capability means that updates, security patches, and other system changes can be deployed without direct access to the physical devices.
4.Real-Time Updates: endpoint security solutions can automatically push updates and patches to ensure that all devices are protected against the latest known threats.
5. Authentication and Access Control: The software can authenticate login attempts to prevent unauthorized access. It can also control which users have access to specific applications and data.
6. Threat Detection and Response: If a threat is detected, the endpoint security can take immediate action, such as blocking the execution of unsafe applications, quarantining infected files, or alerting administrators.
7. Data Encryption: To prevent data loss or theft, endpoint security software can encrypt sensitive information, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
8. Integration with Other Security Tools: endpoint security often integrates with other security tools, such as intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. This integration allows for a more comprehensive defense, where potential breaches can be detected and prevented before they occur.
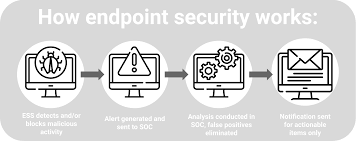

How does Endpoint Security work
What Are the Components of Endpoint Security Software?
1. Firewall: A firewall acts as a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks, such as the Internet. It monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules, deciding whether to allow or block specific traffic.
2. Endpoint security Platforms (EPP): EPPs offer a suite of security features designed to protect endpoints from various threats. This includes malware and ransomware protection, application control, patch management, analytics, anomaly detection, web and email security, and data encryption.
3. Exploit and Threat Protection: This component focuses on preventing exploits and threats from reaching the endpoint. It often involves signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and behavior monitoring to identify and block malicious activities before they can cause harm.
4. Network Protection: Network protection within the context of endpoint security involves safeguarding network assets from threats that may originate from or target endpoints. This can include network-level intrusion prevention systems (IPS) and network segmentation to limit the spread of threats.
5. Application Protection: Application control is a feature that restricts the execution of unauthorized or potentially harmful applications. It helps enforce security policies by allowing only approved applications to run on endpoints.
6. Data Protection: Data protection features, such as encryption, ensure that sensitive data remains confidential and integrity is maintained even if the data is intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties.
7. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR is a more advanced component that provides real-time monitoring and analysis of endpoint activities to detect, investigate, and respond to threats that evade traditional defenses. EDR solutions often include threat hunting capabilities and automated response actions.
8. Intelligence and Analytics: Endpoint security software leverages threat intelligence and analytics to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security incident. This component helps in proactive threat detection and enables a faster response to incidents, improving the overall security posture of the organization.


The Key Components of Endpoint Security Software
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Endpoint Security vs Antivirus:
Endpoint Security: Provides a comprehensive suite of security measures to protect all connected devices from a broad spectrum of threats. It includes features like real-time monitoring, threat response, data encryption, and more.
Antivirus: Primarily focuses on detecting and removing known viruses and malware. It is a subset of endpoint security, offering basic protection against specific types of threats.
2. VPN as Endpoint Security:
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is not an endpoint security solution itself but can be considered part of a comprehensive endpoint security strategy. VPNs secure the data transmission between endpoints and the corporate network, and modern VPNs can conduct security checks to ensure endpoints meet certain security postures before allowing access.
3. Definition of Endpoint Security:
Endpoint security refers to the measures taken to protect devices like desktops, laptops, mobile phones, and tablets from malicious threats and cyberattacks. It involves a combination of software, hardware, and procedural controls to safeguard endpoints.
4. Difference Between Endpoint (EPP) and EDR:
Endpoint security Platform (EPP): Offers fundamental security functions such as malware scanning, removal, and basic threat detection.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Provides more advanced functionality, including the detection, analysis, and response to security incidents, often involving real-time monitoring and automated threat hunting.
5. Difference Between Endpoint Security and Defender:
Windows Defender: The default security client for Microsoft Windows, providing basic protection against malware and viruses.
Microsoft Defender: A broader suite of security tools that includes Windows Defender for Endpoint, designed for enterprise security, especially for those with Microsoft 365 licenses.
6. Difference Between Cloud and Endpoint Security:
Traditional Endpoint Security: Managed directly on the device, providing local protection and control.
Cloud-based Endpoint Security: Relies on cloud infrastructure for real-time protection and centralized management, offering scalability and the ability to update defenses rapidly across all endpoints.
7. Difference Between VPN and Endpoint:
A VPN creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device (endpoint) and a server, routing all internet traffic through this tunnel.
An endpoint refers to the devices at either end of the VPN tunnel, such as your computer or the server you are connecting to.
8. Examples of Endpoints:
Endpoints can include mobile devices, desktop computers, virtual machines, embedded devices, servers, and IoT devices like cameras, smart speakers, and thermostats.
9. What is Considered Endpoint Security:
Endpoint security encompasses the practices and technologies used to secure endpoints or entry points of end-user devices against exploitation by malicious actors. It includes a range of tools and strategies to protect devices on a network or in the cloud from cybersecurity threats.
Related Articles
What are Automotive Relays & How it Works
Thyristor Controlled Reactor (TCR) and Thyristor Switched Capacitor (TSC)
Different Types of Audio Cables and How to Pick the Right One
Lithium CR1620 Battery: Application and Features
Introduction to Optical Sensor
Introduction to Battery CR1220
Introduction to HDMI Modulator
JMBom Electronics, a company that collaborates with various manufacturers, supplies a broad array of electronic components. Their product lineup includes semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes, integrated circuits (ICs), and resistors. This article has been brought to you by JMBom Electronics. Should you seek further details regarding their products, please visit their website.
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













