

How Does A Fuel Pressure Regulator Work?
Catalog
What Is a Fuel Pressure Regulator?And How Does A Fuel Pressure Regulator Work?How does the diaphragm move within the Fuel Pressure Regulator?What are the essential parts of a Fuel Pressure Regulator?Should I upgrade my Fuel Pressure Regulator?What is the purpose of a Fuel Pressure Regulator?Why the Fuel Pressure Regulator is Important?Signs of a Failing Fuel Pressure RegulatorRelated ArticlesWhat Is a Fuel Pressure Regulator?And How Does A Fuel Pressure Regulator Work?
While you may not be familiar with the term "fuel pressure regulator," it's a crucial component of any EFI system; without it, your vehicle won't function. The fuel pressure regulator ensures that the fuel rail maintains sufficient pressure to deliver the right amount of fuel to the injectors. Without it, fuel could bypass the system entirely, failing to reach the injectors.
If the fuel tank's pass-through becomes completely blocked, excessive fuel could flood the injectors, leading to their failure. To achieve the correct air-fuel mixture in all driving scenarios—from idling to high RPMs—the fuel pressure regulator plays a vital role, adjusting to meet fuel demand.
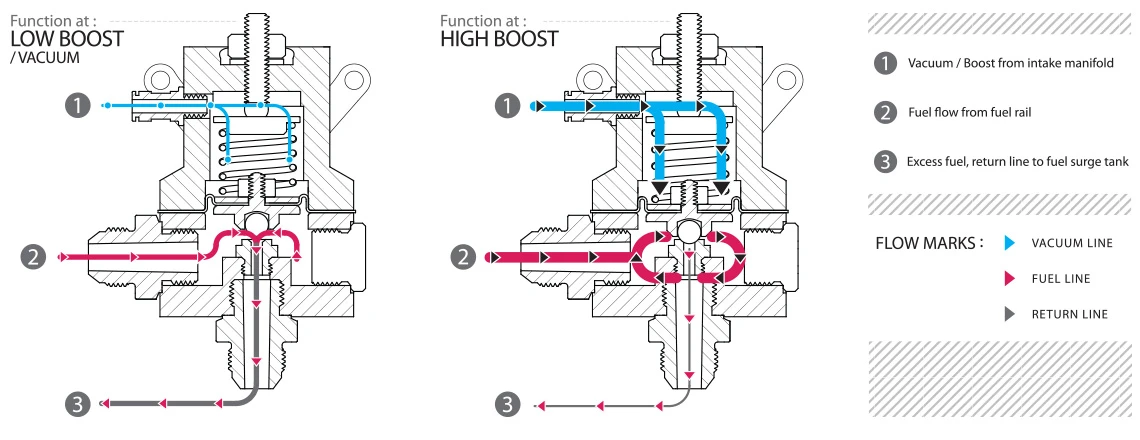
This regulator guarantees a steady fuel supply, even during significant changes in fuel demand, ensuring proper fuel flow. The fuel injector has two sides: one side receives pressure from the fuel rail, while the other side is boosted by a compressor or turbo. The ideal fuel-to-air ratio is 1:1. The fuel pressure regulator manages fuel pressure in relation to air pressure or boost, allowing the injector to maintain this ratio effectively.
It features a diaphragm that controls a bypass valve, also known as the ball seat, which opens and closes to ensure consistent fuel delivery. When boost pressure is applied to the regulator, the diaphragm, attached to the bypass valve, is pushed down by a spring, limiting excess fuel flow. This action makes the fuel pump work harder, increasing fuel pressure as intake manifold boost rises.
How does the diaphragm move within the Fuel Pressure Regulator?
What are the essential parts of a Fuel Pressure Regulator?

Should I upgrade my Fuel Pressure Regulator?
We frequently receive inquiries about our Fuel Pressure Regulator, including its operation, its role within a fuel system, and why we confidently assert that it can handle over 1000 HP.
In this guide, we will cover the fundamentals: how it works, its functionality in a fuel system, and the various components involved. Many existing online resources are outdated, focusing on older designs that often do not apply to modern injection systems. Therefore, we decided to create our own guide featuring sleek, easy-to-understand graphics to bridge this gap.
What is the purpose of a Fuel Pressure Regulator?
The Fuel Pressure Regulator is essential for any EFI system; without it, the fuel rail cannot generate enough pressure to deliver the right amount of fuel to the injectors, resulting in fuel bypassing the system altogether. Conversely, if the pass-through to the fuel tank is completely blocked, the fuel pump may push too much fuel into the injectors, leading to their failure.
To ensure a proper air-fuel mixture, adequate fuel pressure is necessary in all situations, whether at low or high RPMs, regardless of power output. This is where the fuel pressure regulator plays a crucial role, adjusting the fuel supply to meet demand.
Why the Fuel Pressure Regulator is Important?
Engine Performance: A properly functioning regulator enhances engine responsiveness and power output. When the regulator maintains optimal pressure, the engine can efficiently combust the fuel, leading to better acceleration and overall performance.
Fuel Efficiency: By keeping the right fuel pressure, the regulator helps optimize fuel consumption. An efficient fuel system reduces waste and saves you money at the pump, making it an essential part of cost-effective driving.
Emission Control: An efficient combustion process reduces harmful emissions. A good regulator ensures that the fuel-air mixture is balanced, helping your vehicle meet environmental standards and contributing to a cleaner atmosphere.
Signs of a Failing Fuel Pressure Regulator
Be vigilant for warning signs that your fuel pressure regulator may be failing:
- Poor Acceleration: If your vehicle struggles to accelerate or feels sluggish, it could indicate that the regulator isn't maintaining proper pressure.
- Stalling: Frequent stalling, especially after starting the engine or during low-speed driving, can suggest irregular fuel supply due to a malfunctioning regulator.
- Increased Fuel Consumption: A sudden spike in fuel costs may indicate that your regulator is not efficiently controlling fuel flow, leading to excessive consumption.
- Check Engine Light: If your check engine light illuminates, it may be a sign of a fuel system issue, including a faulty regulator.
This article is from JMBom Electronics which offer electronic components, semiconductors, antennas, capacitors, connectors, diodes, transistors, ICs, and resistors. For more product information, please go to the website to get it.
Related Articles
LR41 Battery Equivalent-A Complete Guide
A Complete Guide to 357 Battery Equivalent
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













