

Guide to Corner Reflector
Catalog
What is a Corner Reflector?What is the Purpose of a Corner Reflector?How Does a Corner Reflector Work?Types of Corner ReflectorsCorner Reflector CalculationAdvantages of Corner ReflectorsDisadvantages of Corner ReflectorsApplications of Corner ReflectorsSummaryRelated ArticlesA corner antenna is designed to reflect incoming electromagnetic signals from an external source. These antennas are commonly used at higher microwave frequencies, making them popular in spacecraft antenna systems due to their simple structure and lightweight design. Corner antennas come with various types of reflectors, including parabolic, ellipsoid, hyperbolic, or spheroid shapes. Common types of corner antennas include plane, rod, corner, spherical, parabolic, and cylindrical. This article will give you a brief overview of the corner reflector.
What is a Corner Reflector?
A corner reflector is a passive device that reflects radio signals directly back towards the emission source. It’s a type of retroreflector made up of three flat surfaces that meet at right angles, reflecting waves back to the source, although with some transformation. These surfaces are usually square in shape. Corner reflectors are widely used in radar calibration.
Made from metal plates or wires arranged at right angles, these reflectors have a unique ability to reflect electromagnetic waves. As a result, they appear as bright targets on a radar display, even if they are off to the side or far away. Corner reflectors are often used as reference points or markers for radar measurements, such as speed, distance, position, or angle.
Examples of corner reflectors include radar corner reflectors and optical corner reflectors. A radar corner reflector is typically made of metal and is designed to reflect radio signals from radar systems. On the other hand, optical corner reflectors, also known as corner cubes or cube corners, are made from three-sided glass prisms. These are commonly used in applications like laser ranging and surveying.
What is the Purpose of a Corner Reflector?
A corner reflector is used to generate a strong radar echo, especially from objects that would typically have a low effective radar cross-section (RCS). The reflector consists of at least two electrically conductive surfaces mounted at right angles to each other. The larger the corner reflector, the more energy it will reflect.
How Does a Corner Reflector Work?
A corner reflector operates based on the principles of optics, meaning the reflected signal travels in the same direction as the incoming one. Specifically, when an electromagnetic signal strikes a corner reflector, it gets reflected off each electrically conductive surface. In a dihedral structure, the signal is reflected twice, while in a trihedral structure, it's reflected three times. This results in the direction of the waves being reversed, causing them to reflect back towards their source. Because of this behavior, the corner reflector is considered a passive device.
Reflectors are commonly used in antennas to improve their directivity. The primary purpose of a corner-shaped reflector in an antenna is to help focus the radiated energy onto the metal plate, enhancing the directivity by reflecting the energy in the desired direction.
Corner Reflector Antenna
A corner reflector antenna is a directional antenna commonly used at UHF and VHF frequencies. It was invented in 1938 by John D. Kraus. The antenna consists of a dipole-driven element placed in front of two flat rectangular reflecting panels, typically arranged at a 90° angle.
These antennas offer moderate gain (10 to 15 dB), a high front-to-back ratio (20 to 30 dB), and a wide bandwidth.
Corner reflector antennas are widely used in applications such as UHF television point-to-point communication links, receiving antennas, data links for WANs, and amateur radio on the 144 MHz, 420 MHz, and 1296 MHz bands. They radiate linearly polarized radio waves, and can be mounted for either vertical or horizontal polarization.
Types of Corner Reflectors
There are two main types of corner reflectors: dihedral and trihedral. Let's take a closer look at each:
Dihedral Corner Reflector
A dihedral corner reflector is a corner antenna with two surfaces placed on orthogonal planes. It consists of two plane reflectors that form a 90° dihedral angle. This type of reflector is created when two conducting sheets are joined perpendicularly and is commonly used in antennas.
The dihedral corner reflector reflects the wave back towards the emission source only when the incident beam is perpendicular to the intersection line of the two planes. In this setup, the wave is reflected twice. One drawback of these reflectors is that they are sensitive to their mechanical alignment, meaning misalignment can lead to performance issues.
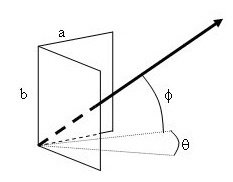
Dihedral Type
Trihedral Corner Reflector
A trihedral corner reflector is a corner antenna that has three surfaces positioned on orthogonal planes. It is formed by connecting three conducting sheets in a perpendicular orientation. In this setup, the wave is reflected three times. Trihedral reflectors are commonly used in radar systems due to their ability to efficiently reflect signals back toward the source.
This trihedral corner reflector is highly tolerant to misalignment, making it ideal for quick field setup and calibration when needed. When radio waves strike the corner of the reflector, they are reflected off each of the three surfaces, resulting in a wave that is reflected three times. This causes the wave to be transmitted back to the source in an inverted direction.
As a result, the trihedral reflector provides a high Radar Cross Section (RCS), making it an excellent target for radar system testing, data collection, and calibration for various applications.
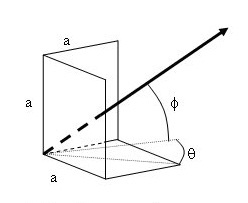
Trihedral Type
These trihedral reflectors are standard radar reflectors commonly used to calibrate or assess the performance of radar systems. They offer several key advantages, including a large radar cross-section (RCS), the ability to reflect signals from a wide range of aspect angles, and a theoretical RCS that can be easily calculated based on the aspect angle.
Corner Reflector Radiation Pattern
The diagram below illustrates the radiation pattern of a vertical corner reflector along its main axis. In antenna design, the radiation pattern refers to the directional distribution of radio wave strength emitted by the antenna. It’s a graphical representation of the antenna's far-field properties, showing how the radiated power varies depending on the direction relative to the antenna.
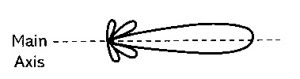
Radiation Pattern of Corner Reflector
Corner Reflector Calculation
The corner reflector is a valuable tool for radar system calibration. It typically consists of perpendicular plates that intersect at right angles. The two most common types of corner reflectors are trihedral and dihedral.
While dihedral corner reflectors are sensitive to mechanical alignment, trihedral corner reflectors are highly tolerant of misalignment. This makes them an ideal choice for quick setup and calibration in the field. The design of this reflector is simple, typically made from three right-angle plates, as shown in the figure below.
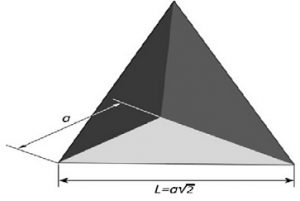
Reflector with Three Right Angle Plates
The effective area (Aeff) of a trihedral corner reflector can be calculated using the formula:Aeff=a23A_{\text{eff}} = \frac{a^2}{\sqrt{3}}Aeff=3a2
Where ‘a’ is the side length of the trihedral reflector.
The effective radar cross-section (σ) can be measured using the following equation:σ=4πa43λ2\sigma = \frac{4 \pi a^4}{3 \lambda^2}σ=3λ24πa4
Where ‘λ’ is the wavelength of the radar signal.
In the trihedral corner reflector, the waves strike the corner and are reflected off each surface three times. This results in waves that are reflected back towards the source in a reversed direction. As a result, this type of reflector provides a very high Radar Cross Section (RCS), making it an excellent target for radar system testing and characterization.
Advantages of Corner Reflectors
- Broad Bandwidth Gain: Corner reflectors, especially at the lower end of the UHF band, provide broad bandwidth gain.
- High Gain: They offer high gain, allowing them to transmit and receive signals over long distances.
- Stronger Reflection: The more surfaces a corner reflector has, the stronger the reflection.
- Ideal for Microwaves & UHF: These reflectors are particularly effective at microwaves and ultra-high frequencies, where structures with dimensions of one or two wavelengths are practical.
- Simple Construction: Their design is simple, making them easy to deploy, inexpensive, and portable.
- No Power or Maintenance: Corner reflectors don’t require any power source, calibration, or regular maintenance.
- Flexible Orientation: They can be arranged in various orientations and locations.
- Target Simulation: By adjusting the shape, number, and size of the reflectors, they can be used to simulate various targets such as vehicles, aircraft, or buildings.
- Reliable Radar Reference: They serve as a dependable reference for radar performance evaluation.
- Radar Calibration: Corner reflectors help check the sensitivity, accuracy, and resolution of radar systems, aiding in the identification and correction of errors.
Disadvantages of Corner Reflectors
- Bulky Setup: The presence of corner reflectors can make antenna arrangements bulky and cumbersome.
- Increased Cost: Using corner reflectors increases the overall cost of the antenna system.
- Not Real-World Targets: While useful for radar validation, corner reflectors are not representative of real-world targets.
- Limited Scenario Coverage: They may not fully capture the range of challenges and scenarios a radar system would encounter in practice.
- Interference Risks: Corner reflectors used for radar validation might interfere with other radar systems or users.
- Radar Clutter: They can create clutter or false alarms on radar displays, potentially masking or confusing other targets.
- Regulatory Issues: The use of corner reflectors may violate regulations or permissions regarding airspace or radar frequency usage.
Applications of Corner Reflectors
- Radar Systems: Corner reflectors are used in radar systems to hide the presence of defense vehicles from enemy radar detection.
- TV Signal Reception: These reflectors are commonly used in home antennas for TV signal reception.
- Optical Communication: Corner reflectors find applications in optical communication systems.
- Radar Validation: When used correctly, they are valuable for radar system validation and testing.
- UHF and VHF Applications: They are widely used for UHF TV receiving antennas, data links for wireless WANs, point-to-point communication links, and amateur radio on the 1296, 144, and 420 MHz bands.
- Reflecting Electromagnetic Waves: Corner reflectors are used to reflect radio waves and other electromagnetic waves directly back to the emission source.
- Radar Echo Generation: These reflectors generate strong radar echoes from objects that would otherwise have very low effective radar cross-sections (RCS).
- Security Applications: They are used to create reflectors for bicycles, signs, and cars to enhance visibility.
- Laser Ranging: Corner reflectors are also used for bouncing laser beams back toward Earth from the moon's surface.
Summary
A corner reflector is a retroreflector with three mutually perpendicular and intersecting flat surfaces, often in square shapes. These reflectors are typically made from metal for reflecting radar waves, while optical corner reflectors are made from three-sided glass prisms for uses such as surveying and laser ranging.
Related Articles
Diode Dynamics: Real-World Behavior in Fast Power and RF Circuits
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













