
Overview of Embedded Software and Programming
Catalog
Components of Embedded SystemsEmbedded SoftwareEmbedded System Programming LanguagesProgramming an Embedded System in Assembly LanguageAdvantages of Using C in Embedded SystemsAdvantages and DisadvantagesFrequently Ask QuestionsRelated ArticlesAn embedded system is essentially a combination of hardware and software designed to carry out a specific task, usually within a set time frame. For instance, a washing machine is an embedded system since it’s built to perform just one function. The key benefits of using an embedded system in various applications are reduced size, lower cost, and improved reliability and efficiency. This article gives an overview of embedded software languages, embedded system programming, and their roles.
Components of Embedded Systems
Here are the key components that make up embedded systems
- Embedded Hardware: The microcontroller is the central unit of the system, with various peripherals connected to it for communication.
- Embedded RTOS (Real-Time Operating System): This system handles complex tasks and ensures real-time operation.
- Device Drivers: These act as intermediaries between the operating system and peripheral devices, allowing them to interact smoothly.
- Communication Stacks: These are used to facilitate communication with external devices.
- Embedded Applications: These are the specific functions that the embedded device is programmed to perform.
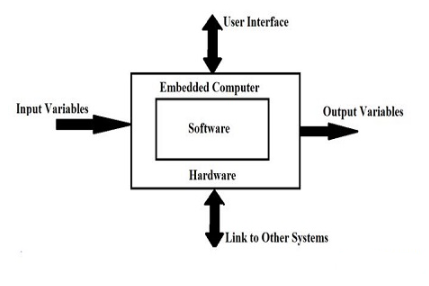
Embedded System Components
Embedded Software
Embedded software, also known as embedded system programming, is computer software designed to control devices by providing a set of instructions. Often referred to as firmware, it’s used to program a wide variety of devices with different functionalities, all while maintaining key design constraints like response times, strict deadlines, and data processing requirements. The final data is typically stored in memory, such as RAM or ROM.
This software is controlled or triggered through a machine interface. Embedded software is found in nearly all electronic devices—like cars, phones, robots, and security systems—and is often designed to run on simple 8-bit microcontrollers with only a few kilobytes of memory. It’s responsible for processing complex tasks and ensuring accurate computations.
Embedded System Programming Languages
Embedded software often uses a real-time operating system (RTOS) that can perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Programs are commonly written in languages like C, C++, Python, and JavaScript, and are processed on operating systems such as Linux, VxWorks, Fusion RTOS, Nucleus RTOS, micro C/OS, OSE, and others.
The choice of programming language plays a critical role in embedded software development and is influenced by several factors, including:
- Size: The amount of memory needed by the program is crucial, as embedded processors (like microcontrollers) have a limited amount of ROM (Read-Only Memory) based on their specific application.
- Speed: The program needs to execute quickly.
- Portability: It’s ideal if a program can be compiled for different processors.
- Implementation: Can be challenging depending on the complexity.
- Maintenance: Can be difficult, especially as the system grows.
Programming an Embedded System in Assembly Language
Programming an embedded system in assembly language involves writing instructions that are then converted into machine-level code using an assembler. Here’s an example where we add two numbers using two separate registers and store the result in an output register:
Input:
HERE: MOV R0, #01H
MOV R1, #02H
MOV A, R0
ADD A, R1
MOV P0, A
SIMP HERE
Output (Assembly Code):
| Address | Opcode | Operand |
|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 78 | 01 |
| 0002 | 79 | 02 |
| 0004 | E8 | – |
| 0005 | 29 | – |
| 0006 | F5 | 80 |
| 0008 | 80 | 00 |
Assembly language is useful for developing efficient code in terms of size and speed. However, writing large programs in assembly can be difficult, leading to higher software development costs. Additionally, code portability can be a problem. To address these challenges, higher-level languages like embedded C are often used.
C, C++, Java, and Embedded C
C Programming
The C language, developed by Dennis Ritchie, is a structured programming language known for its efficiency. It provides minimal memory access through a simple compiler and allows data to be processed efficiently based on machine instructions. C is used in a wide range of applications, from embedded systems to supercomputers.
Embedded C
Embedded C is an extension of the C language specifically designed for programming embedded systems. While the syntax remains similar to standard C (including functions, data type declarations, loops, etc.), there are key differences. Embedded C focuses on hardware input-output addressing, fixed-point operations, and managing address spaces.
Advantages of Using C in Embedded Systems
- It is small, easy to learn, and simple to debug.
- All C compilers are compatible with a wide range of embedded devices.
- It is processor-independent, meaning it works across different microprocessors and microcontrollers.
- C combines the power of assembly language with the flexibility of high-level programming.
- It is efficient, reliable, and portable across different platforms.
- Programs written in C are easier to understand, debug, and maintain.
- Compared to other high-level languages, C is more flexible due to its small, structured design and support for low-level bitwise operations.
C++
C++ is an object-oriented programming language, but it may not always be the best choice for efficient programming in resource-constrained environments like embedded systems. While C++ features like virtual functions and exception handling provide powerful programming tools, they can be inefficient in terms of memory and processing speed for embedded systems.
Java
Java can be used for programming embedded systems, especially when paired with a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). It is mainly used in high-end applications, such as mobile phones, and offers portability across different systems. However, Java is not typically preferred for smaller embedded devices due to its relatively high resource usage.
Embedded C Programming Architecture and Example
The architecture of Embedded C programming can be illustrated using an example with the 8051 microcontroller. In this case, the task is to blink an LED connected to PORT1 of the controller. The code below uses the Keil C Compiler to perform this task.
Example Code to Blink an LED:
#include <reg51.h> // Pre-processor directive
void delay(int); // Delay function declaration
void main(void) // Main function
{
P1 = 0x00; // Turn off PORT1, so the LED is off
while(1) // Infinite loop
{
P1 = 0xFF; // Turn on PORT1, so the LED is on
delay(1000); // Delay to keep LED on for a moment
P1 = 0x00; // Turn off PORT1
delay(1000); // Delay to keep LED off for a moment
}
}
void delay(int d) // Delay function implementation
{
unsigned int i = 0; // Local variable for the delay loop
for (; d > 0; d--) // Loop for the specified delay time
{
for (i = 250; i > 0; i--); // Inner loop to create delay
for (i = 248; i > 0; i--); // Additional delay for finer control
}
}
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of Embedded Software:
- Faster data loading: Embedded systems are optimized for quick data processing.
- Lower cost: Since they’re specialized, embedded systems tend to be more cost-effective.
- Efficient resource usage: These systems require fewer resources, making them efficient.
Disadvantages of Embedded Software:
- Complex upgrades: Updating embedded software can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Frequent resets: In case of problems, you may need to reset the system regularly.
- Scalability issues: Embedded systems can be difficult to scale, particularly for small values or devices.
Applications of Embedded Software:
- Banking: Used in ATMs and secure transactions.
- Automobiles: Controls functions like airbags, engine management, etc.
- Home Appliances: Embedded systems are found in devices like washing machines, microwaves, and refrigerators.
- Cars: Used for infotainment systems, safety features, and more.
- Missiles: Embedded systems manage guidance, control, and navigation.
Frequently Ask Questions
1) What is Embedded Software?
Embedded software, also known as embedded system programming, is computer software designed to control devices by providing a set of instructions.
2) What programming languages are used in Embedded System Software?
Embedded system software is typically written in languages like C, C++, Python, and JavaScript.
3) What’s the difference between embedded systems and normal systems?
An embedded system combines hardware and software, designed to perform a specific task. It processes tasks sequentially. On the other hand, a normal system, often using a real-time operating system (RTOS), is capable of parallel execution for tasks that require multitasking.
4) What are the different types of Embedded Systems?
Embedded systems can be classified in two main ways:
- By performance and functionality: These include real-time, stand-alone, networked, and mobile systems.
- By the performance of the microcontroller: These are categorized as small-scale, medium-scale, and sophisticated systems.
5) Major applications of Embedded Systems
Some major applications of embedded systems include:
- Washing machines
- Digital cameras
- Music players
An embedded system is a combination of hardware and software. Various programming languages are used for different purposes, such as controlling the performance of machines or computers. While a programmer has multiple language options, C, C++, Python, and JavaScript are commonly used in embedded software development. These systems often run on platforms like Linux OS, micro C/OS, and QNX. C language is the foundation for writing embedded software code. This is a general overview of embedded software and its architecture, demonstrated with a sample program.
Related Articles
Honeywell Zephyr™ Airflow Sensor: Specifications, Usage, and Safety
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













