

2SC5200 Transistor: Overview, Pinout, and Common Uses
Catalog
What Is the 2SC5200 Transistor?Pin ConfigurationFeatures and Specifications of the 2SC5200 TransistorHow to Use the 2SC5200 Transistor (with Circuit Diagram)Working PrincipleApplicationsSpecial Use Case:Frequently Ask QuestionsRelated ArticlesThe 2SC5200 is a high-power NPN transistor commonly used in general-purpose switching and audio power amplifier circuits. It features three terminals—emitter, base, and collector—and consists of three semiconductor layers in an N-P-N structure, with the P-type layer sandwiched between two N-type layers.
This article provides a comprehensive introduction to the 2SC5200 transistor, including its pin configuration, how it works, and its typical applications.
What Is the 2SC5200 Transistor?
The 2SC5200 is a high-performance NPN transistor commonly used in audio frequency (AF) amplifiers and high-power audio applications due to its high current handling capability and strong current gain. Originally developed by Toshiba, it remains widely available and is often paired with its complementary PNP counterpart, the TTA5200.
This transistor comes in a durable TO-264 package, made from a combination of epoxy and plastic materials, making it suitable for various amplifier designs. It supports a collector-emitter voltage (V<sub>CE</sub>) of up to 230V and can handle a continuous collector current of 30A. Typical applications include televisions, mobile devices, flip-flop circuits, and industrial control systems.

When operating at high collector currents and switching frequencies, the 2SC5200 transistor tends to generate significant heat. For this reason, it is typically mounted with a heat sink to prevent the circuit from overheating and ensure stable performance.
In many amplifier designs, the 2SC5200 is paired with its complementary PNP transistor, the 2SA1943. This pairing is commonly used in push-pull amplifier configurations—especially in Class B and Class AB amplifiers—where both NPN and PNP transistors work together to deliver high output power with improved efficiency.
Pin Configuration
The 2SC5200 transistor has three pins, each with a specific function. Below is a description of each terminal along with the corresponding symbol representation:
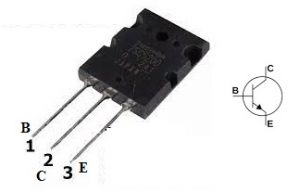
2SC5200 Transistor Pin Configuration
- Pin 1 (Base): Used to control the transistor’s operation by providing the necessary biasing signal. It turns the transistor ON or OFF.
- Pin 2 (Collector): The main current flows into the transistor through this terminal. It is typically connected to the load.
- Pin 3 (Emitter): This is where the current exits the transistor. It is usually connected to ground in common circuit configurations.
Features and Specifications of the 2SC5200 Transistor
The 2SC5200 is a high-power NPN transistor with the following key features and electrical specifications:
Key Features:
- High-power NPN transistor
- Packaged in a TO-264 case for efficient heat dissipation
- Supports large current handling capacity
- Ideal for high-fidelity (Hi-Fi) audio frequency amplifier output stages
- Simple to drive (easy to turn ON and OFF)
- Suitable for both low and high-frequency applications, particularly in audio amplification
- Low power loss when in the ON state
- Low harmonic distortion, ensuring clear audio performance
- High transition frequency for fast switching
Electrical Specifications:
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 55 to 160
- Transition Frequency (fT): 30 MHz
- Collector Current (IC): 15 A (continuous)
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (V<sub>CE</sub>): 230 V
- Collector-Base Voltage (V<sub>CB</sub>): 230 V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (V<sub>BE</sub>): 5 V
- Base Current (I<sub>B</sub>): 1.5 A
- Power Dissipation (P<sub>D</sub>): 150 W
- Polarity: NPN
- Operating Temperature Range: -55°C to +150°C
Equivalents and Replacements
Several transistors can serve as equivalents or replacements for the 2SC5200, depending on the application:
- Equivalent Transistors: 2SD1313, 2SC5242, 2SC3320, and FJL4315
- Replacement Options: MJL3281A, KTC5242, TTC5200, and MJL13002A
- Complementary Transistor: 2SA1943 (PNP type, commonly used in push-pull amplifier designs with 2SC5200)
Please note that the 2SC5200 is a through-hole (THT) device, and no SMD (Surface-Mount Device) version is available for this transistor.
How to Use the 2SC5200 Transistor (with Circuit Diagram)
An audio amplifier is an electronic circuit designed to increase the amplitude of weak AC or DC signals. These circuits are commonly found in devices like mono and stereo speakers, home audio systems, and various amplification modules. Below is a basic audio amplifier circuit built using the 2SC5200 NPN power transistor.
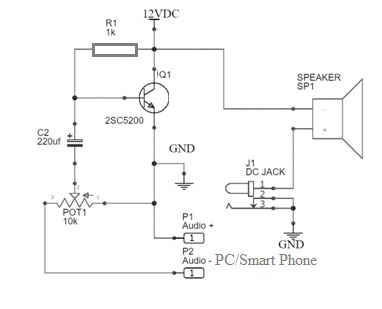
Audio Amplifier Circuit using 2SC5200 Transistor
Circuit Components:
- 1 × 2SC5200 NPN power transistor
- 1 × 0.5W, 8Ω speaker
- 1 × 3.5mm audio input jack (male or female)
- 1 × 10K potentiometer (for input level control)
- 1 × 1K resistor
- 1 × 220µF electrolytic capacitor
- 1 × 12V DC power supply
- Battery clips, jumper wires, and a breadboard
Working Principle
The circuit receives its audio input from a device such as a smartphone or computer via a 3.5mm audio jack. This signal passes through a 10K potentiometer, which adjusts the input voltage level, functioning as a volume control.
A 220µF capacitor is placed in series with the input to block any DC component from the signal, allowing only the AC portion (the actual audio signal) to pass through. This AC signal is then fed to the base of the 2SC5200 transistor, where it acts as a control signal.
As the transistor amplifies the input signal, the larger current flow between the collector and emitter terminals drives the connected 8Ω speaker, producing a louder output sound.
The amplified output signal is taken from the collector terminal of the 2SC5200 transistor and routed to the negative terminal of the speaker. The positive terminal of the speaker is connected to the positive rail of the DC power supply, typically through a 3.5mm DC power jack.
To prevent the transistor from overheating during operation—especially under high current loads—a heat sink is recommended for thermal management, though it may be optional in low-power setups.
Applications
This audio amplifier circuit has a wide range of applications:
- Music Production: Commonly used in recording and audio enhancement systems in the music industry.
- Military Use: Applied in acoustic weapon systems due to its ability to generate powerful audio signals.
- Radar & Communication: Utilized in HVAC radar systems and other high-frequency audio-based technologies.
Applications of the 2SC5200 Transistor
The 2SC5200 is a versatile NPN power transistor widely used in various high-current and audio-related applications. Some of its common uses include:
- Audio frequency (AF) amplifier circuits
- Medium-power switching applications
- AF and RF signal circuits
- High-current switching loads (up to 15A)
- Low slew-rate device designs
- Push-pull amplifier configurations
- High-power audio amplifier circuits
- Circuits requiring high current operation
- High-fidelity (Hi-Fi) audio systems
- Voltage regulation circuits
- Medium-power electronic circuits
Special Use Case:
The 2SC5200 is especially popular in 200W stereo amplifier systems, capable of handling audio frequencies ranging from 5 Hz to 100 kHz with a sensitivity of 0.75 Vrms. Thanks to its low signal-to-noise ratio and minimal harmonic distortion, it delivers clean, high-quality sound—making it ideal for precision audio applications.
The 2SC5200 is a high-power NPN transistor commonly used in audio frequency (AF) amplifiers and other high-power audio circuits, thanks to its excellent current gain. However, when operating continuously under heavy loads, the transistor can generate significant heat, which may degrade its performance over time. To prevent overheating and maintain reliability, a heat sink is typically employed.
This transistor is marked with a unique three-digit lot number along with an underline beneath it, indicating whether the device is lead-free or compliant with RoHS standards.
Frequently Ask Questions
Is the 2SC5200 a Transistor or a MOSFET?
The 2SC5200 is a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) — specifically, an NPN power transistor, not a MOSFET.
2SC5200 vs. TTC5200: What’s the Difference?
| Feature | 2SC5200 | TTC5200 |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Toshiba (original) | Toshiba |
| Gain (hFE) Range | ~80–160 | Slightly lower or similar |
| Notes | Widely used in audio amplifiers | Slight variant, same applications |
| Appearance | Different marking/silkscreen | May be used as drop-in replacement |
They’re functionally similar — both are NPN power BJTs and often used interchangeably in high-power audio circuits.
MOSFET vs. BJT (like 2SC5200)
| Feature | MOSFET | BJT (e.g., 2SC5200) |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Field Effect Transistor (voltage-driven) | Bipolar Junction Transistor (current-driven) |
| Speed | Faster switching | Slower |
| Efficiency | Higher | Lower in switching circuits |
| Input Drive | Needs voltage | Needs current |
| Applications | SMPS, digital circuits | Audio amplifiers, analog control |
2SC5200 Technical Specs (Key)
- Type: NPN BJT Power Transistor
- Max Collector Current (Ic): 15 A
- Max Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): 230 V
- Base Voltage (Vbe): ~1.5 V typical
- Power Dissipation: 150 W
- Applications: Audio Frequency (AF) amplifiers, high-power audio systems
- Package: TO-264
Summary
- 2SC5200 is a BJT, not a MOSFET.
- TTC5200 is nearly identical to 2SC5200 — used in the same way.
- MOSFETs are generally faster and more efficient for switching; BJTs like 2SC5200 excel in linear amplification (e.g., audio).
Related Articles
Capacitive Sensors : How They Work and Where They’re Used
How Voltage Sensors Work and Their Common Applications
How Do Distance Sensors Work and Where Are They Used?
Throttle Position Sensors: How They Work and Where They're Used
How Inductive Sensors Work and Where They're Used
How a Flame Sensor Works and Where It's Used
How a Flex Sensor Works and Where It's Used
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













