
Voltage Amplifier: Circuit Design, Gain, vs. Power Amplifier, and Key Applications
Catalog
What Is a Voltage Amplifier?Voltage GainVoltage Amplifier CircuitDifference Between Voltage Amplifier and Power AmplifierDifference Between Current Amplifier and Voltage AmplifierApplications of Voltage AmplifiersFrequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Voltage AmplifiersRelated ArticlesAn amplifier is an electronic component designed to boost the current, voltage, or power of a signal while preserving its original waveform. Amplifiers are widely used across various fields including wireless communication, broadcasting, and audio systems. They come in many forms—ranging from operational amplifiers and small-signal amplifiers to high-power amplifiers.
Amplifiers are generally categorized by their function into two main types: voltage amplifiers and power amplifiers. This classification depends largely on factors like signal strength, circuit configuration, and how the input signal interacts with the power source and the load.This article explores the basics of voltage amplifiers, how they work, and where they’re typically used.

What Is a Voltage Amplifier?
A voltage amplifier is a type of amplifier designed to increase the voltage level of an input signal without significantly altering its waveform. These amplifiers are essential when transmitting voltage signals over longer distances or when the signal needs to be processed by other components.
The primary function of a voltage amplifier is to enhance the voltage of an electrical signal while maintaining its original characteristics. They play a critical role in electronic systems by enabling cleaner audio, crisper visual output, and more precise sensor data.
While a voltage amplifier doesn't supply power in the way a power amplifier does, it increases the available voltage in a circuit to achieve the necessary signal strength. Though not typically used to drive high-power loads like motors, voltage amplifiers are ideal for amplifying weak signals from sensors or control systems.
Voltage Gain
A voltage amplifier is a type of amplifier primarily designed to increase the voltage level of an input signal. The core objective of this amplifier is to achieve the highest possible voltage gain. Voltage gain refers to the ratio of the amplifier’s output voltage to its input voltage, which determines how effectively the amplifier boosts the input signal.
The voltage gain (Av) of an amplifier is calculated using the formula:
Av = Vout / Vin
These amplifiers typically consume very little power from the connected load. Because the input signals they handle are usually very small in amplitude, these amplifiers are also known as small-signal amplifiers. Their main function is to amplify these low-level signals without significantly drawing power or altering the signal’s characteristics.
Voltage Amplifier Circuit
The circuit design for a voltage amplifier is relatively straightforward, as it only requires a few basic electronic components. These amplifiers are sometimes referred to as differential voltage amplifiers because they amplify the voltage difference between two points in a circuit. As a result, the varying output voltage can be easily measured and interpreted for further analysis or processing.
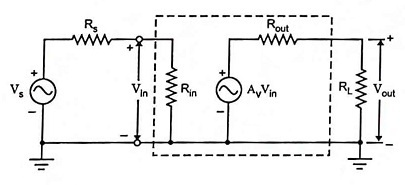
Voltage Amplifier Circuit
Voltage Amplifier Circuit Operation
The voltage amplifier circuit, as illustrated above, takes an input voltage signal, amplifies it, and delivers a corresponding output voltage. This type of amplifier functions as a voltage-controlled voltage source. For optimal performance, the amplifier should have a high input impedance and a low output impedance.
In the circuit, if the input resistance (Rin) is much greater than the source resistance (Rs), then the input voltage (Vin) is approximately equal to the source voltage (Vs):
Vin ≈ Vs
Similarly, if the load resistance (RL) is much greater than the output resistance (Rout), then:
Vout ≈ Av × Vin
Where the voltage gain Av is:
Av = Vout / Vin ≈ Vout / Vs
In an ideal voltage amplifier, the input resistance is considered infinite, and the output resistance is zero. This ensures that the amplifier delivers an output voltage that is directly proportional to the input voltage, regardless of the source and load resistances. The proportional relationship remains constant, unaffected by variations in the connected components.
Difference Between Voltage Amplifier and Power Amplifier
Both voltage amplifiers and power amplifiers serve the purpose of boosting an input signal, but they do so in different ways depending on the application. A voltage amplifier is designed to increase the voltage level of a signal, often with minimal power gain. In contrast, a power amplifier is built to deliver significant power gain, making it suitable for driving high-power loads such as speakers or transmitters.
While voltage amplifiers are commonly used to strengthen weak signals for further processing, power amplifiers are typically employed where large amounts of current and power are needed to operate output devices.
Both types of amplifiers are widely used in audio systems and radio frequency (RF) applications. The key distinctions between them are outlined below.
| Voltage Amplifier | Power Amplifier |
| An amplifier that is designed to amplify an input signal’s voltage is known as a voltage amplifier. | An amplifier that is designed to provide a considerable quantity of power gain for the input signal is known as a power amplifier. |
| This amplifier enhances input signals the amplitude without providing considerable power gain. | This amplifier uses a low-power electrical signal & enhances its power level to make it appropriate for driving high-power loads or loudspeakers. |
| It is also called a small signal amplifier because it has a small magnitude input signal. | The power amplifier is known as a large signal amplifier because that needs a large magnitude input signal. |
| In this amplifier circuit, the transistor base is thin because it is not designed to handle the huge current. | The transistor base in this amplifier circuit is fairly thicker which handles large currents. |
| The transistor used in this amplifier is a low (or) medium power transistor which has a small physical size | The transistor used in this amplifier is a high-power transistor which has a large physical size |
| The collector current value in this amplifier is quite low that is 1 mA. | The collector current value in this amplifier is high, around 100 mA. |
| The amount of AC o/p power given by this amplifier is low. | The amount of AC o/’p power given by this amplifier is high |
| The current gain of this amplifier is low. | The current gain of this amplifier is high. |
| It is coupled with RC. | The current amplifier is coupled with the transformer. |
| Heat dissipation is low. | Heat dissipation is high. |
| These amplifiers are used frequently in audio equipment to amplify the signal without increasing its power significantly. | Power amplifiers are used commonly in wireless communication systems, audio systems, and various scientific & industrial applications wherever high output power is necessary. |
Difference Between Current Amplifier and Voltage Amplifier
Both current amplifiers and voltage amplifiers are electronic components designed to amplify electrical signals, but they operate based on different principles and serve different purposes.
A voltage amplifier increases the voltage level of an input signal, typically with high input impedance and low output impedance. On the other hand, a current amplifier is designed to boost the current of a signal, usually featuring low input impedance and high output impedance.
These differences make each type suitable for specific applications, and the key distinctions are summarized below.
| Current Amplifier | Voltage Amplifier |
| An amplifier that is used to enhance the input signal’s current by maintaining stable voltage is known as a current amplifier. | An amplifier that is used to enhance the input signal’s voltage by maintaining a stable current is known as a voltage amplifier. |
| This amplifier allows a little input current to control a larger output current. | This amplifier allows a little input voltage to control a larger output voltage. |
| The input and output of this amplifier are current with low input impedance and high output impedance. | The input and output of this amplifier is voltage with high input impedance & low output impedance. |
| It is used for voltage amplification. | The current amplifier is used for current amplification. |
| This amplifier has extremely high voltage gain, input impedance & less output current. | This amplifier has low voltage gain, large current gain, and medium range to high i/p impedance. |
Applications of Voltage Amplifiers
Voltage amplifiers are widely used across various fields due to their ability to boost the voltage level of an input signal. Some common applications include:
- Signal amplification: Used to increase the output voltage amplitude of low-level input signals.
- Consumer electronics: Commonly found in a wide range of electronic devices.
- Communication systems: Employed in wireless communication, broadcasting, and audio systems like loudspeakers and headphones.
- Long-distance signal transmission: Ideal for applications requiring voltage transmission over long cables, where maintaining signal strength is essential.
- Audio equipment: Used in speaker systems to amplify audio signals and in radios to strengthen weak signals received by antennas.
- Impedance matching and switching: Useful in circuits that require impedance matching or act as part of a switching mechanism.
In summary, voltage amplifiers are crucial components in electronic systems where low-voltage input signals need to be converted into higher-voltage outputs for effective processing or transmission.
They are especially valuable when maximum signal voltage is needed over extended distances.
Question for you: What is an amplifier?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Voltage Amplifiers
What is a voltage amplifier?
A voltage amplifier is an electronic circuit designed to take an input voltage signal and produce an amplified version of it at the output. The amplification is measured by the voltage gain, which is the ratio of output voltage to input voltage.
What’s the difference between a current amplifier and a voltage amplifier?
A current amplifier is optimized to increase the current of a signal. It features low input impedance and high output impedance. In contrast, a voltage amplifier is designed to boost voltage levels, with high input impedance and low output impedance. Each is suited to different load and source conditions.
How do you amplify voltage?
Voltage can be amplified using a transistor-based amplifier circuit, provided it's configured correctly. You’ll also need a secondary power source that can support the desired output voltage level. For AC signals, transformers can also be used to step up or down voltage.
How does a voltage amplifier work?
At its simplest, a voltage amplifier increases the voltage of an input signal. It does this by drawing energy from an external power supply to boost the signal’s voltage level while maintaining its shape and frequency characteristics.
What does a voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) do?
A Voltage-Controlled Amplifier (VCA) or Variable-Gain Amplifier (VGA) adjusts its gain depending on a control voltage (CV). VCAs are widely used in audio compression, synthesizers, and modulation systems, where dynamic control of amplification is needed.
Why do we need amplifiers?
Amplifiers—especially in audio systems—boost weak signals so they can drive speakers, headphones, or other output devices. Whether you’re playing audio from a laptop, turntable, or CD player, an amplifier ensures the signal is strong enough for audible output.
Why aren’t voltage amplifiers used as power amplifiers?
Power amplifiers are designed to deliver high current and power to heavy loads and often use transformer coupling. Voltage amplifiers, in contrast, operate with low collector current (typically around 1 mA), and use transistors with thin base regions suited for voltage gain but not high power output.
Why is an op-amp considered a voltage amplifier?
An Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) is an integrated circuit that amplifies the voltage difference between its two input terminals. While it's called an operational amplifier due to its ability to perform mathematical operations, it essentially functions as a high-gain voltage amplifier and forms the building block for many analog circuits such as filters, buffers, and comparators.
Related Articles
Infineon ILD8150E LED Driver IC Overview
LF353N Op-Amp Explained: Pinout, Features, and How It Works
ADXL335 Accelerometer Sensor: Pinout, Specs, Features, and How It Works
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor: Overview, Function & Circuit Design
Crankshaft Position Sensor: Overview, Circuit Function& Comparison with Camshaft Sensors
Inverting Summing Amplifier: Circuit Diagram,Operation and Formula
Active Bandpass Filter: Overview, Types,Q Factor & Applications
Passive High-Pass Filter: Overview, Circuit Design & Transfer Function
Differential Pressure Sensors: Working Principle, Interfacing,Testing Methods and Common Issues
Subscribe to JMBom Electronics !













